
The abundance of single-use plastic items such as water bottles, grocery bags, and packaging materials has soared since the 1950s. These objects break down into microplastics, or tiny bits of plastic less than 5 millimeters long (less than half the width of your pinky fingernail), which are now ubiquitous.
No one knows exactly how much microplastic has made it into the environment, but in 2021, an international team of multidisciplinary scientists estimated that there were 24.4 trillion pieces of microplastics in the world's upper oceans alone, or the equivalent of roughly 30 billion plastic water bottles.
Because of their minute size, microplastics aren't easy to track. For many years, researchers assumed these tiny bits of trash entered rivers, where they were carried downstream to the ocean in a relatively short amount of time. But that's not actually the case. According to a new study published in Science Advances, it's estimated that microplastics may remain in rivers for more than 300 years before entering the ocean. This means the microplastics in rivers have much greater potential to cause harm to humans and the environment than scientists previously thought.
هذه القصة مأخوذة من طبعة May - June 2022 من Popular Mechanics.
ابدأ النسخة التجريبية المجانية من Magzter GOLD لمدة 7 أيام للوصول إلى آلاف القصص المتميزة المنسقة وأكثر من 9,000 مجلة وصحيفة.
بالفعل مشترك ? تسجيل الدخول
هذه القصة مأخوذة من طبعة May - June 2022 من Popular Mechanics.
ابدأ النسخة التجريبية المجانية من Magzter GOLD لمدة 7 أيام للوصول إلى آلاف القصص المتميزة المنسقة وأكثر من 9,000 مجلة وصحيفة.
بالفعل مشترك? تسجيل الدخول

ONE OF THE 'GREATEST THREATS' TO THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST ISN'T WHAT YOU THINK.
EXPERTS ARE PREPARING THE REGION AGAINST THE THREAT OF DANGEROUS VOLCANIC MUDFLOWS, KNOWN AS LAHARS, WHICH COULD INUNDATE THE COMMUNITIES SURROUNDING MT. RAINIER IN AS LITTLE AS 30 MINUTES.

THE WORLD'S TOUGHEST ROW
They rowed 3,000 miles across the Atlantic, battling unpredictable weather, chaotic seas, and finicky equipment. But what they discovered gave them profound new insights into the power of the ocean.

HOW TO DIY OFF-GRID SOLAR
SPEND THE TIME UP FRONT AND PLAN IT CAREFULLY TO AVOID DISAPPOINTMENT
Are We on the Verge of an ARMS RACE in SPACE?
RUMORS OF A RUSSIAN SPACE NUKE, ALONG WITH OTHER SATELLITE-TARGETING WEAPONS, HAVE MADE GEOPOLITICAL TENSIONS EXTEND INTO ORBIT.

Fresh Fingerprints on an Ancient Statue
A CLAY FIGURINE HAS SPENT MILLENNIA incomplete, waiting at the bottom of a lake for its long-dead craftsman to finish the Iron Age-era statuette.

Quantum Entanglement in Our Brains
IT HAS LONG BEEN ARGUED THAT THE human brain is similar to a computer. But in reality, that's selling the brain pretty short.

The Tools of Copernicus
WAY BACK IN 1508, WITH ONLY LIMited tools at his disposal, Nicolaus Copernicus developed a celestial model of a heliocentric planetary system, which he described in hist landmark work De revolutionibus orbium coelestium. It was a complete overhaul of our conception of the universe-one that, unfortunately, earned him the ire of the Catholic church for decades after his death-and forever changed the way we look at the stars.

Building a Sixth-Generation Bomber Raptor
THE GLOBAL COMBAT AIR Programme (GCAP)-a project by the U.K., Italy, and Japan to develop a sixth-generation stealth fighter-has been busy at the drawing board reshaping its vision of the future of air warfare. And judging by the new concept model unveiled at this year's Farnborough air show, that future has big triangular wings.

The Electroweak Force of the Early Universe
TODAY, THE UNIVERSE AS WE KNOW IT IS governed by four fundamental forces: the strong nuclear force, the weak nuclear force, electromagnetism, and gravity.
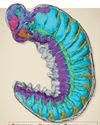
This Ancient Fossil With a Brain and Guts
WE KNOW WHAT FOSSILS LOOK like. For example, typical dinosaur fossils are bones turned to stone and preserved from the passage of time, located, if we're particularly lucky, in large collections that can be reassembled to represent the beast they used to prop up in their entirety.