
PCR is a laboratory (in-vitro) technique that is employed Pfor amplifying a targeted portion of DNA. This technique is a cell-free method utilized to synthesize several identical copies of a gene or DNA of interest. Thus, it is a very essential tool in a molecular biology laboratory synonymous to a photocopier as a basic requirement in an office. First, we will outline the requirements for a standard PCR reaction – the following will be needed: DNA polymerase enzyme, magnesium chloride (MgCl2), nucleotides, primers, nuclease free water, target DNA template to be amplified and a PCR machine. The PCR reaction mechanism is simple and starts with an initial Denaturation where the double-stranded DNA is heated to separate the strands (1st step) this allows for the primers to attach to the now single stranded DNA (2nd step). After the primers align to the DNA strand, the DNA polymerase enzyme extends the primers (3rd step) which results into two identical copies of the original DNA template. These three steps are repeated over a series of temperatures and times a single complete process of the three combined is known as an amplification cycle. It is important to optimize every step of the cycle to the DNA template and the set of primers being used. The cycles can be repeated as many times as needed, however, on average a standard PCR is run for around 30 to 40 times after which the amplified product is then analyzed. The polymerase chain reaction is used to amplify a targeted DNA of interest for downstream experimental purposes; and it has also found immense use in detection of pathogenic DNA as well as other applications in genetic testing. PCR is a very sensitive technique as tiny volumes of a single reaction are required, as such it is recommended that a master mix is prepared if there are many reactions.
هذه القصة مأخوذة من طبعة September - October 2020 من Scientific India.
ابدأ النسخة التجريبية المجانية من Magzter GOLD لمدة 7 أيام للوصول إلى آلاف القصص المتميزة المنسقة وأكثر من 9,000 مجلة وصحيفة.
بالفعل مشترك ? تسجيل الدخول
هذه القصة مأخوذة من طبعة September - October 2020 من Scientific India.
ابدأ النسخة التجريبية المجانية من Magzter GOLD لمدة 7 أيام للوصول إلى آلاف القصص المتميزة المنسقة وأكثر من 9,000 مجلة وصحيفة.
بالفعل مشترك? تسجيل الدخول

An insight into Chandipura virus in India
Recently lot of news regarding disease due to Chandipura virus has emerged in various newspapers/magazines. After reading the reports published it seems that thing is still brewing in the natures nest and it could affect mankind.

Why elephants never forget?
An elephant has a very large brain for its size and the 'temporal lobe' region responsible for memory is more developed with a greater number of folds - this results in powerful abilities to 'download' important survival data such as where to find food and water, and who is friend or foe.

Use of Algae for Wastewater Treatment Containing Heavy Metals
Wastewater treatment is a critical environmental issue particularly when it comes to the removal of heavy metals.

Nano priming Seeds: A Small Innovation Sparkling Big Advances in Germination
Nanopriming is an emerging agricultural technique where the seeds are treated with nanoparticles to improve their germination, growth, and overall performance.
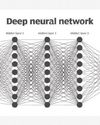
Nobel Laureates in Physics 2024: Revolutionizing AlThe Physics Foundations Behind Machine Learning
This year's two Nobel Laureates in Physics have used tools from physics to develop methods that are the foundation of today's powerful machine learning.
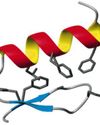
Revolutionizing Biology: The 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry Celebrates Breakthroughs in Protein Design and Structure Prediction
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2024 is about proteins, life's ingenious chemical tools.
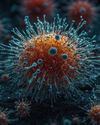
New findings on animal viruses with potential to infect humans
Scientists investigating animal viruses with potential to infect humans have identified a critical protein that could enable spillover of a family of organisms called arteriviruses.

Father-Daughter Team Decodes Mars' Alien Signal
There is no definitive answer to whether aliens exist, but there is a lot of work being done to find out:
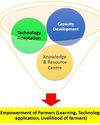
Krishi Vigyan Kendras: Working for Farmer's Welfare
Krishi Vigyan Kendras (Farm Science Centres) are the District level institution serving as an agriculture knowledge resource & capacity development centre which plays indispensable role in front line extension regarding agriculture system in scientific way.

Sixth generation Computer: The future computing technology
We are in a transition towards a digital world, where everything will be dealt with in digital format.