
We don't yet know whether reports of immune complications in one or two trial participants have been linked to the COVID-19 vaccine itself, or if they were given the placebo vaccine.
But it does highlight the importance of phase 3 clinical trials in many thousands of people, across continents. These not only tell us whether a vaccine is safe, but also whether it works for people of different ages or with particular health issues.
So what are some of the immune factors that determine whether any of the 180 or so COVID-19 vaccine candidates being developed around the world actually work?
Our immune responses are all different
An effective vaccine should generate long-lasting protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
This can be by generating antibodies to neutralise the virus and likely also by helping the immune system memorise and quickly respond to infection.
We know, from developing vaccines against other viruses, that people's immune response to a vaccine can vary. There's every reason to believe this will also be the case for a COVID-19 vaccine.
Dr Paul Gill, Postdoctoral Researcher (Gastroenterology and Immunology), Monash University, Melbourne, Australia.
Menno van Zelm, Associate Professor, Immunology, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia.
1. Vaccine type and how it's delivered
هذه القصة مأخوذة من طبعة September - October 2020 من Scientific India.
ابدأ النسخة التجريبية المجانية من Magzter GOLD لمدة 7 أيام للوصول إلى آلاف القصص المتميزة المنسقة وأكثر من 9,000 مجلة وصحيفة.
بالفعل مشترك ? تسجيل الدخول
هذه القصة مأخوذة من طبعة September - October 2020 من Scientific India.
ابدأ النسخة التجريبية المجانية من Magzter GOLD لمدة 7 أيام للوصول إلى آلاف القصص المتميزة المنسقة وأكثر من 9,000 مجلة وصحيفة.
بالفعل مشترك? تسجيل الدخول

Building world's 1st pyramid
In a preprint study published this summer, researchers proposed that ancient Egyptians built the world's first pyramid the 4,700-year-old Step Pyramid of Djoser, which sits on Egypt's Saqqara plateau using a \"modern hydraulic system\" powered by a long-gone branch of the Nile River.
Climate change arms the world, ovarian cancer pulls the trigger.It's time we disarm them both
Climate change, driven by human activities, leads to environmental changes such as rising temperatures, altered weather patterns, and increased pollution.

Climate Change Added 18 mph to Hurricane Wind Speeds over Past 5 Years
High ocean temperatures caused by global warming boosted maximum intensities for most storms between 2019 and 2023, as well as for every 2024 hurricane.

How Indian Vulture Decline Led to 500,000 Deaths in 5 Years
Once a common sight across India, vultures were abundant scavengers, often seen circling landfills in search of carcasses.
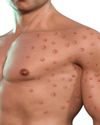
Understanding Monkeypox: Insights and Implications
Monkeypox, a viral zoonotic disease, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its re-emergence and sporadic outbreaks globally.

AI predicts that most of the world will see temperatures rise to 3°C much faster than previously expected
Three leading climate scientists have combined insights from 10 global climate models and, with the help of artificial intelligence (AI), conclude that regional warming thresholds are likely to be reached faster than previously estimated.

Infrared Radiation: A New Player In Mosquito Host-Seeking
The sound of mosquitoes is all around us when the sun sets and the air gets warm and sweltering.

Fish Oil May Benefit to Cure Alzheimer's, disorder: new findings
The benefits of fish and fish oil consumption are well-known in medical science as fish is considered a precious food resource that provides sufficient nutrition to humans.

A new class of antivirals could help prevent future pandemics
The arrival of Paxlovid in December 2021 marked another turning point in the COVID-19 pandemic an effective antiviral that has since successfully treated millions.

Turning carbon emissions into methane fuel
Chemists have developed a novel way to capture and convert carbon dioxide into methane, suggesting that future gas emissions could be converted into an alternative fuel using electricity from renewable sources. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a greenhouse gas that accounts for a large part of Earth's warming climate, and is produced by power plants, factories and various forms of transportation.