
Deep within the lava caves of Hawaii, microbial life thrives. In fact, a recent study has found that the life teeming within the caves is made up almost entirely of unknown species. More surprisingly, the researchers found that the microbial life was structured into complex networks of species that relied on each other. Within these networks were 'hub species', with so many links to other species that if they were removed, it could cause ecological collapse.
HOW DID YOU SEARCH FOR LIFE IN THESE LAVA CAVES?
Dr Rebecca Prescott: We had 70 samples of microbial mats [layers of microbes that live on surfaces] that we looked at from a variety of volcanic environments of different ages. The environments included lava tubes, geothermal caves and steam vents.
In order to identify the microbes, we looked at a gene called the '16S rRNA gene'. It's like a little tag that helps us with identification. We also looked at what microbes were 'hanging out' together, to try to better understand the structure of these communities.
TELL US MORE ABOUT THIS TECHNIQUE.
Dr Stuart Donachie: Prior to 1986, microbiologists could only identify microbes that they'd cultured in the lab. Everything we knew about microbial diversity - meaning how many species there are - was based only on what we could grow in Petri dishes. That gave us a rather narrow view, but it was the best we could do at that time.
In 1986, there was a method developed that involved sequencing [the 16S rRNA gene]. This method is based on extracting as much DNA as possible from the environmental sample, and then making copies of this particular gene. Once this method was applied in the environment, we detected bacteria that had never been seen before.
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der August 2022-Ausgabe von BBC Science Focus.
Starten Sie Ihre 7-tägige kostenlose Testversion von Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierte Premium-Storys sowie über 8.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Bereits Abonnent ? Anmelden
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der August 2022-Ausgabe von BBC Science Focus.
Starten Sie Ihre 7-tägige kostenlose Testversion von Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierte Premium-Storys sowie über 8.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Bereits Abonnent? Anmelden

THE WORST IDEAS OF THE 21ST CENTURY
NOT ALL IDEAS CAN BE HITS. ALONGSIDE GROUND-BREAKING INNOVATIONS, 21ST-CENTURY SCIENTISTS HAVE HELMED THEIR SHARE OF WILD TECH FLOPS, DUBIOUS THEORIES AND OVERHYPED BREAKTHROUGHS. HERE ARE THE BIGGEST TO FORGET

10 IDEAS THAT WILL SHAPE YOUR NEXT 25 YEARS
Predicting the future is considered a fool's game. But it's one many of us like to play.

THE BIGGEST BREAKTHROUGHS OF THE CENTURY
We're a quarter of the way into the new century. To mark this milestone, we asked the UK's top minds to highlight some of the game-changing scientific breakthroughs shaping our world since the year 2000

DO THE SCIENCE COGNITIVE SHUFFLE
Trouble sleeping? A lot on your mind? Use this trick and sedate your synapses
WHAT DETERMINES HOW MANY ABS I CAN GET?
Assuming you're a human being, you have exactly the same number of abs as everybody else: two.

HOW CAN I IDENTIFY MY PSYCHOLOGICAL BLIND SPOT?
In the 1950s two American psychologists, Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham, proposed a way of thinking about psychological blind spots - things you don't know about yourself - that they called the 'Johari Window' (the term is a combination of their first names).

How can I change my personality?
Want to become more confident, extroverted or assertive? Science shows that with a few simple changes, you can unlock your best self

Could your cosmetics be harming your health?
Cosmetic companies are phasing out microplastics and so-called 'forever chemicals' to help protect consumers.

extraterrestrial US Congress is talking about activity again. Is the truth really out there?
Despite several testimonies, the question remains frustratingly unanswered
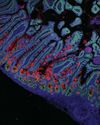
Map of 100 million human body cells revealed
Over three dozen new studies mark significant milestone towards complete Human Cell Atlas