
FOURTEEN YEARS AFTER DUBBING ITS most powerful non-nuclear weapon ever developed "the Mother of All Bombs (MOAB), the U.S. military finally found an opportunity to test the ordnance on the battlefield. In April 2017, intelligence officials had located a large cell of Islamic State Khorasan, the terrorist group also known as ISIS-K, hiding in a cave complex in Nangarhar province on the border with Pakistan.
The GBU-43/B Massive Ordnance Air Blast, to use its official name, had shown promise during demonstrations in testing grounds, such as Eglin Air Force Base in Florida, since its unveiling in 2003. But the Pentagon had never deployed it in actual battle, over concerns about civilian casualties. This cell, however, was believed to be remote enough for a MOAB deployment.
According to the initial assessment by the Afghan Ministry of Defense and local media reports, the surprise blast swept through the caves with ease, causing at least 36 casualties, without harming any known civilians. (The U.S. government never publicly released its own damage assessment.) For the Pentagon, this was more than a strike against terrorists: It served to demonstrate the feasibility of its newly developed weapons systems.
In many ways, Afghanistan was the ideal battleground for trialing new technology. Unlike in Iraq and Syria, much of the fighting took place in rural or mountainous areas with low concentrations of civilians. Using the GBU-43/B near urban centers would constitute a war crime under international law because the force would have been "indiscriminate," causing civilian deaths and the destruction of critical infrastructure.
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der March - April 2022-Ausgabe von Popular Mechanics.
Starten Sie Ihre 7-tägige kostenlose Testversion von Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierte Premium-Storys sowie über 8.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Bereits Abonnent ? Anmelden
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der March - April 2022-Ausgabe von Popular Mechanics.
Starten Sie Ihre 7-tägige kostenlose Testversion von Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierte Premium-Storys sowie über 8.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Bereits Abonnent? Anmelden

ONE OF THE 'GREATEST THREATS' TO THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST ISN'T WHAT YOU THINK.
EXPERTS ARE PREPARING THE REGION AGAINST THE THREAT OF DANGEROUS VOLCANIC MUDFLOWS, KNOWN AS LAHARS, WHICH COULD INUNDATE THE COMMUNITIES SURROUNDING MT. RAINIER IN AS LITTLE AS 30 MINUTES.

THE WORLD'S TOUGHEST ROW
They rowed 3,000 miles across the Atlantic, battling unpredictable weather, chaotic seas, and finicky equipment. But what they discovered gave them profound new insights into the power of the ocean.

HOW TO DIY OFF-GRID SOLAR
SPEND THE TIME UP FRONT AND PLAN IT CAREFULLY TO AVOID DISAPPOINTMENT
Are We on the Verge of an ARMS RACE in SPACE?
RUMORS OF A RUSSIAN SPACE NUKE, ALONG WITH OTHER SATELLITE-TARGETING WEAPONS, HAVE MADE GEOPOLITICAL TENSIONS EXTEND INTO ORBIT.

Fresh Fingerprints on an Ancient Statue
A CLAY FIGURINE HAS SPENT MILLENNIA incomplete, waiting at the bottom of a lake for its long-dead craftsman to finish the Iron Age-era statuette.

Quantum Entanglement in Our Brains
IT HAS LONG BEEN ARGUED THAT THE human brain is similar to a computer. But in reality, that's selling the brain pretty short.

The Tools of Copernicus
WAY BACK IN 1508, WITH ONLY LIMited tools at his disposal, Nicolaus Copernicus developed a celestial model of a heliocentric planetary system, which he described in hist landmark work De revolutionibus orbium coelestium. It was a complete overhaul of our conception of the universe-one that, unfortunately, earned him the ire of the Catholic church for decades after his death-and forever changed the way we look at the stars.

Building a Sixth-Generation Bomber Raptor
THE GLOBAL COMBAT AIR Programme (GCAP)-a project by the U.K., Italy, and Japan to develop a sixth-generation stealth fighter-has been busy at the drawing board reshaping its vision of the future of air warfare. And judging by the new concept model unveiled at this year's Farnborough air show, that future has big triangular wings.

The Electroweak Force of the Early Universe
TODAY, THE UNIVERSE AS WE KNOW IT IS governed by four fundamental forces: the strong nuclear force, the weak nuclear force, electromagnetism, and gravity.
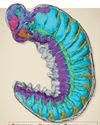
This Ancient Fossil With a Brain and Guts
WE KNOW WHAT FOSSILS LOOK like. For example, typical dinosaur fossils are bones turned to stone and preserved from the passage of time, located, if we're particularly lucky, in large collections that can be reassembled to represent the beast they used to prop up in their entirety.