
The interconnected history of India and China and the circulatory movement of ideas, people, technologies and commodities are well recorded in the textual as well as oral traditions of both countries. Its footprints could be found throughout the geographical landscapes of present-day India, China and beyond, whether it was the birth of Chinese Buddhism or the dissemination of ancient India's astronomy, literature, music and languages into China, or technologies such as sugar making, paper manufacturing and silk production coming from China to India and other countries.
All of it enriched knowledge systems across the world. The translation industry in China, for example, had people from India and many Central Asian polities supporting it, along with hundreds of Chinese scholar monks. Even today, there are 35,000 Sanskrit words in the Chinese language. The Dai, a minority nationality in the Yunnan province, had its own version of the Ramayana.
It was during the colonial period that contemporary images of India and China found their foundations. As Qing China (1636-1912) became apprehensive of the threat from British India, it sent officials to study the decline of the Indian civilisation and the intentions of the British in the Himalayan states. Qing officials such as Huang Maocai, Ma Jianzhong, Wu Guangpei and Kang Youwei lamented the decline of Indian civilisation. Indians were called “people of a lost century” and “no more than slaves”. Lu Xun, one of the greatest modern Chinese writers, despised Rabindranath Tagore as a “poisonous datura” and Indian people as “inferior slaves”. In his opinion, colonised India had become a defeated country and, therefore, it was impossible for it to produce great writers and works any longer.
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der July 21, 2024-Ausgabe von THE WEEK India.
Starten Sie Ihre 7-tägige kostenlose Testversion von Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierte Premium-Storys sowie über 8.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Bereits Abonnent ? Anmelden
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der July 21, 2024-Ausgabe von THE WEEK India.
Starten Sie Ihre 7-tägige kostenlose Testversion von Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierte Premium-Storys sowie über 8.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Bereits Abonnent? Anmelden

Too Much Sitting Can Accelerate Ageing
SITTING FOR EXTENDED PERIODS can harm the heart and accelerate ageing, even if you are young and get the minimum recommended amount of daily exercise, according to a US study published in the journal PLOS One.
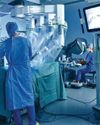
Efficiency and innovation
As health care evolves, professionals must employ innovative methods to refine their skills
Level up
Only 30 per cent of needy patients are able to undergo transplant in India; we need more dedicated transplant centres

HOPE STEMS FROM A CELL
While stem cell therapies have shown success in treating blood disorders, orthopaedic ailments, autoimmune diseases and eye issues, there is hope that they can one day treat patients with heart disease, blindness, Parkinson's, HIV, diabetes and spinal cord injuries

Mind matters
Your mindset can limit or expand your physical ability

Cutting edge
Would you go under the knife if a robot was the one holding it? Or would you say, \"No way, I need a human touch\"? You might have to decide soon because a robot that can imitate skilled human surgeons is already here.
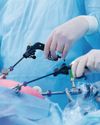
The smallest cut
Minimally invasive surgeries have a bright future, with virtual reality and 3D procedures offering greater precision and AI on the horizon

Signalling a revolution
Canadian scientist and entrepreneur Sachdev Sidhu is focused on bringing cutting-edge antibody engineering to his country of origin

Wellness on demand
Starting as a doctor-patient chat platform, Medibuddy has evolved to be India's largest on-demand, full-stack digital health care platform

HEARING AND VISION LOSS LINKED TO HEART DISEASE AND STROKE
A CHINESE STUDY PUBLISHED IN THE JOURNAL of the American Heart Association suggests that middle aged and older adults with sensory impairments, specifically hearing and vision loss, have an elevated risk of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke and heart attacks.