
In 2023, ChatGPT took off. The online artificial intelligence (AI) tool became so big that even your uncle who doesn't own a smartphone knew about it. But as its owners, OpenAI, continue to polish and improve their prodigy, there's a competitor ready to take over.
Soon after the launch of ChatGPT, Google announced it was working on its own AI tool, Bard. A rival to Open Al's offering, Bard could do all the things ChatGPT could, but with the might of the world's largest search engine behind it.
Now, Google is taking another step forward with its latest AI project: Google Gemini. Currently being rolled out, Gemini is claimed to already be outperforming ChatGPT and it's left plenty of us wondering if Google will take the AI top spot in 2024.
WHAT IS GEMINI AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
When it comes to AI, the application that everyone knows about is ChatGPT. But for that tool to work it needs to be powered by something, that's where GPT-4 comes in. A large language model, GPT-4 is trained on billions of sets of data from the internet to understand images, texts, context and many other factors.
Gemini is to Google what GPT-4 is to OpenAI; it's the artificial intelligence that runs programs like ChatGPT or, in the Case of Google, Bard. Built from the ground up and using teams from across Google, Gemini can generalise and understand content, including text, code, audio, image and video. Like GPT4, Gemini was trained on a massive dataset, including books, articles, code repositories, music, audio recordings and other forms of media.
All this data is broken down into a form that's more understandable to Gemini. The model then learns the relationships between different terms and media, learning how to respond to prompts, questions and proposals.
HOW TO TRY GOOGLE GEMINI FOR FREE
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der March 2024-Ausgabe von BBC Science Focus.
Starten Sie Ihre 7-tägige kostenlose Testversion von Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierte Premium-Storys sowie über 8.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Bereits Abonnent ? Anmelden
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der March 2024-Ausgabe von BBC Science Focus.
Starten Sie Ihre 7-tägige kostenlose Testversion von Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierte Premium-Storys sowie über 8.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Bereits Abonnent? Anmelden

THE WORST IDEAS OF THE 21ST CENTURY
NOT ALL IDEAS CAN BE HITS. ALONGSIDE GROUND-BREAKING INNOVATIONS, 21ST-CENTURY SCIENTISTS HAVE HELMED THEIR SHARE OF WILD TECH FLOPS, DUBIOUS THEORIES AND OVERHYPED BREAKTHROUGHS. HERE ARE THE BIGGEST TO FORGET

10 IDEAS THAT WILL SHAPE YOUR NEXT 25 YEARS
Predicting the future is considered a fool's game. But it's one many of us like to play.

THE BIGGEST BREAKTHROUGHS OF THE CENTURY
We're a quarter of the way into the new century. To mark this milestone, we asked the UK's top minds to highlight some of the game-changing scientific breakthroughs shaping our world since the year 2000

DO THE SCIENCE COGNITIVE SHUFFLE
Trouble sleeping? A lot on your mind? Use this trick and sedate your synapses
WHAT DETERMINES HOW MANY ABS I CAN GET?
Assuming you're a human being, you have exactly the same number of abs as everybody else: two.

HOW CAN I IDENTIFY MY PSYCHOLOGICAL BLIND SPOT?
In the 1950s two American psychologists, Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham, proposed a way of thinking about psychological blind spots - things you don't know about yourself - that they called the 'Johari Window' (the term is a combination of their first names).

How can I change my personality?
Want to become more confident, extroverted or assertive? Science shows that with a few simple changes, you can unlock your best self

Could your cosmetics be harming your health?
Cosmetic companies are phasing out microplastics and so-called 'forever chemicals' to help protect consumers.

extraterrestrial US Congress is talking about activity again. Is the truth really out there?
Despite several testimonies, the question remains frustratingly unanswered
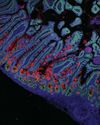
Map of 100 million human body cells revealed
Over three dozen new studies mark significant milestone towards complete Human Cell Atlas