
Turkey berry, a humble yet potent shrub recognized scientifically as Solanum torvum (Fig. 1), has long been embedded in the fabric of traditional medicine across various cultures. Revered for its therapeutic properties, this plant is more than just an agricultural curiosity; it is a cornerstone of herbal remedies passed down through generations. In the lush landscapes where it grows, from the warm regions of Africa to the vibrant fields of Southeast Asia, turkey berry has been harvested and utilized by herbalists and traditional healers who recognize its significant medicinal value (Ogwu et al., 2023).
The adage "Mother Earth's medicine chest is full of healing herbs of incomparable worth" profoundly echoes the enduring importance of plants like turkey berry in natural medicine. In contemporary times, this traditional berry is crossing the threshold into modern medical research, where its potential benefits are being scientifically explored and validated. This exploration not only reinforces ancient wisdom but also opens new avenues for addressing modern health challenges through natural solutions. As we delve deeper into the uses of turkey berry, from its role in ancient healing practices to its emerging significance in modern health science, we uncover a narrative of resilience, versatility, and a promising horizon in the realm of natural therapeutics. This plant has long been rooted in the traditions of local cultures where it is cultivated, not only for its culinary uses but also for its medicinal properties. Essential nutrients such as amino acids, minerals, fatty acids, and vitamins, encompassing both macro and micronutrients, are abundantly present in turkey berry, making it a significant component of traditional medicine systems.
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der July-August 2024-Ausgabe von Scientific India.
Starten Sie Ihre 7-tägige kostenlose Testversion von Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierte Premium-Storys sowie über 8.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Bereits Abonnent ? Anmelden
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der July-August 2024-Ausgabe von Scientific India.
Starten Sie Ihre 7-tägige kostenlose Testversion von Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierte Premium-Storys sowie über 8.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Bereits Abonnent? Anmelden

Building world's 1st pyramid
In a preprint study published this summer, researchers proposed that ancient Egyptians built the world's first pyramid the 4,700-year-old Step Pyramid of Djoser, which sits on Egypt's Saqqara plateau using a \"modern hydraulic system\" powered by a long-gone branch of the Nile River.
Climate change arms the world, ovarian cancer pulls the trigger.It's time we disarm them both
Climate change, driven by human activities, leads to environmental changes such as rising temperatures, altered weather patterns, and increased pollution.

Climate Change Added 18 mph to Hurricane Wind Speeds over Past 5 Years
High ocean temperatures caused by global warming boosted maximum intensities for most storms between 2019 and 2023, as well as for every 2024 hurricane.

How Indian Vulture Decline Led to 500,000 Deaths in 5 Years
Once a common sight across India, vultures were abundant scavengers, often seen circling landfills in search of carcasses.
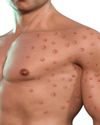
Understanding Monkeypox: Insights and Implications
Monkeypox, a viral zoonotic disease, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its re-emergence and sporadic outbreaks globally.

AI predicts that most of the world will see temperatures rise to 3°C much faster than previously expected
Three leading climate scientists have combined insights from 10 global climate models and, with the help of artificial intelligence (AI), conclude that regional warming thresholds are likely to be reached faster than previously estimated.

Infrared Radiation: A New Player In Mosquito Host-Seeking
The sound of mosquitoes is all around us when the sun sets and the air gets warm and sweltering.

Fish Oil May Benefit to Cure Alzheimer's, disorder: new findings
The benefits of fish and fish oil consumption are well-known in medical science as fish is considered a precious food resource that provides sufficient nutrition to humans.

A new class of antivirals could help prevent future pandemics
The arrival of Paxlovid in December 2021 marked another turning point in the COVID-19 pandemic an effective antiviral that has since successfully treated millions.

Turning carbon emissions into methane fuel
Chemists have developed a novel way to capture and convert carbon dioxide into methane, suggesting that future gas emissions could be converted into an alternative fuel using electricity from renewable sources. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a greenhouse gas that accounts for a large part of Earth's warming climate, and is produced by power plants, factories and various forms of transportation.