
Billionaires are jetting themselves into space and quantum computing lies around the corner. Yet one of the most familiar and everyday aspects of human nature remains frustratingly tricky for scientists to study – dreaming.
Theories abound, but the truth is we don’t really know much about why or how we dream. A major hurdle for scientists has been the fact that when people are dreaming, they’re largely closed off from the world, at least that’s been the assumption for a long while. So researchers have resorted to asking people, upon awakening, what their mind was doing while they were sleeping, but that’s a sketchy and unreliable approach.
“Memories of dreams can be missing some parts of dreams and can be distorted and incorrect, so if that’s all we have to go on, then building a solid science of dreaming will be difficult,” says Dr Ken Paller, a psychologist and dream researcher at Northwestern University.
What would change the whole dream research landscape would be if there were some way to communicate and interact with someone while they were dreaming. It sounds far-fetched, like something out of the Christopher Nolan movie Inception, but in a significant breakthrough, that’s exactly what an international team of researchers, led by Paller and Karen Konkoly also at Northwestern University, managed to achieve. The work, which was published in the journal Current Biology earlier this year, “opens up the opportunities for scientific explorations of dreaming considerably,” says Paller. “We now have more ways to learn about dreaming.”
Esta historia es de la edición September 2021 de BBC Focus - Science & Technology.
Comience su prueba gratuita de Magzter GOLD de 7 días para acceder a miles de historias premium seleccionadas y a más de 9,000 revistas y periódicos.
Ya eres suscriptor ? Conectar
Esta historia es de la edición September 2021 de BBC Focus - Science & Technology.
Comience su prueba gratuita de Magzter GOLD de 7 días para acceder a miles de historias premium seleccionadas y a más de 9,000 revistas y periódicos.
Ya eres suscriptor? Conectar

THE WORST IDEAS OF THE 21ST CENTURY
NOT ALL IDEAS CAN BE HITS. ALONGSIDE GROUND-BREAKING INNOVATIONS, 21ST-CENTURY SCIENTISTS HAVE HELMED THEIR SHARE OF WILD TECH FLOPS, DUBIOUS THEORIES AND OVERHYPED BREAKTHROUGHS. HERE ARE THE BIGGEST TO FORGET

10 IDEAS THAT WILL SHAPE YOUR NEXT 25 YEARS
Predicting the future is considered a fool's game. But it's one many of us like to play.

THE BIGGEST BREAKTHROUGHS OF THE CENTURY
We're a quarter of the way into the new century. To mark this milestone, we asked the UK's top minds to highlight some of the game-changing scientific breakthroughs shaping our world since the year 2000

DO THE SCIENCE COGNITIVE SHUFFLE
Trouble sleeping? A lot on your mind? Use this trick and sedate your synapses
WHAT DETERMINES HOW MANY ABS I CAN GET?
Assuming you're a human being, you have exactly the same number of abs as everybody else: two.

HOW CAN I IDENTIFY MY PSYCHOLOGICAL BLIND SPOT?
In the 1950s two American psychologists, Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham, proposed a way of thinking about psychological blind spots - things you don't know about yourself - that they called the 'Johari Window' (the term is a combination of their first names).

How can I change my personality?
Want to become more confident, extroverted or assertive? Science shows that with a few simple changes, you can unlock your best self

Could your cosmetics be harming your health?
Cosmetic companies are phasing out microplastics and so-called 'forever chemicals' to help protect consumers.

extraterrestrial US Congress is talking about activity again. Is the truth really out there?
Despite several testimonies, the question remains frustratingly unanswered
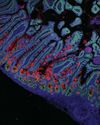
Map of 100 million human body cells revealed
Over three dozen new studies mark significant milestone towards complete Human Cell Atlas