
FOR MANY TEENS, driver’s education class is a rite of passage. It’s the first step toward passing a test, scoring a license, and feeling truly independent behind the wheel. If driverless vehicles catch on, will cars have to take driver’s ed too?
That’s a joke with some truth to it. Because to succeed, a driverless vehicle (or more precisely, that vehicle’s onboard computer) will need to learn all skills that, until now, only human drivers have known.
A Lot to Cover
Onboard computers have to learn the rules of the road, plus all the skill and judgement human motorists use when driving. That includes everything from accelerating and changing lanes to parking and sharing the road with bikes. Sure, computers are “smarter” than people in many ways. But this won’t be easy. If you had to write it all down, even simple driving tasks would require long, detailed instructions. Yet that’s exactly what programming a driverless car will require.
How can we do it? Think science. Most of the actions that we call “driving” are based on physics and other scientific disciplines. So, in a way, driver’s ed is really a special kind of science class—where practicing driving is the lab! And we can use what we know about science to teach vehicles to drive themselves. Let’s test how that could work, using a classic driving situation.
Brake Time
You’re driving along, and the car ahead of you comes to a sudden stop. Now you need to stop your car at a safe distance behind the other vehicle to avoid an accident. How does a human driver accomplish this? Let’s examine the two most important factors.
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

A 12-Year-Old Girl's Election Sticker Is a Winner
VOTING IS A FUNDAMENTAL FREEDOM FOR AMERICANS, A MEANS OF DOING ONE'S CIVIC DUTY AND A WAY AN INDIVIDUAL CAN EXPRESS THEIR VOICE. In 1971, the United States lowered its voting age to 18. But that doesn't mean kids and teens under 18 can't participate in elections in various ways.
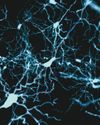
If everything the human brain does is basically sets of electrical impulses, how exactly does that translate into a state of mind?
You're not the only one asking this question. Every neuroscientist in the world is wondering the exact same thing, says Zach Mainen

EARTH'S TINIEST BUILDERS
THE HIDDEN WORLD OF MICROBES IN THE EARTH'S CRUST

MUMMIES SPEAK
ABOUT MICROBES, MIGRATION, AND MORE

GOING WITH YOUR GUT
HOW DO MICROBES AFFECT OUR HEALTH? LET'S COUNT THE WAYS...

BUG Detective
A burglar sneaks into a house on a quiet street in New York City. He walks through the house, touching countertops and door handles. Finally, he steals a single card from a full deck. Then he leaves.

Little Creatures Among Us THE MANY MICROBES IN OUR DAILY LIVES
When you think you're alone, you're actually not. In the ground, the air, your room, and even your body are Strillions and trillions of creatures so tiny you can't see them.

A Mars Rock Found With Leopard Spots Could Be a Sign of Ancient Life
IN JULY, NASA'S PERSEVERANCE ROVER CAME ACROSS A SPOTTED ROCK IN WHAT WAS ONCE A RIVERBED IN THE JEZERO CRATER ON MARS.

Para Athlete Uses Exoskeleton Suit to Carry the Olympic Torch
In July, a 36-year-old French tennis para athlete, Kevin Piette, got a chance to participate in this summer’s Olympic torch relay without using a wheelchair.

Ancient Egyptians May Have Used a Water System to Lift Stones to Build Pyramid
HOW ANCIENT EGYPTIANS BUILT THE MASSIVE PYRAMIDS IN EGYPT MORE THAN 4,000 YEARS AGO HAS LONG BEEN A TOPIC OF WONDER AND DEBATE.