
For thousands of years, the oil palm – indigenous to West Africa – has had an intimate relationship with people. An explosive expansion of oil palm groves throughout western and central Africa in the wake of a dry period around 2 500 years ago enabled human migration and agricultural development; in turn, humans facilitated oil palm propagation through seed dispersal and slash-and-burn agriculture.
Archaeological evidence shows that palm fruit and their oil already formed an integral part of West African diets 5 000 years ago.
With the exception of ‘royal’ oil palm plantations, established in the 18th century for palm wine in the Kingdom of Dahomey, all of West Africa’s oil palms grew in wild and semi-wild groves.
Women and children collected loose fruits from the ground, while men harvested fruit bunches by climbing up to the top of the palms. The fruit was then processed into palm oil by women, through a time-consuming and labour-intensive process involving repetitively boiling and filtering the fresh fruit with water. Similar methods are still widely used throughout West Africa.
While pure red palm oil was derived from the palm fruit’s fleshy outer mesocarp, women also, often with the help of children, cracked the palm kernels to make brown, clear palm kernel oil.
A KEY INGREDIENT IN FOOD
Palm oil was, and remains, a key ingredient in West African cuisine, including the simple dish of boiled yam, palm oil and Kanwa salt, and Banga soup.
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

Agripreneur wins top award for butternut coffee
Bloemfontein-based agripreneur Chantelle de Bruyn has achieved global recognition.

Final fresh produce inquiry pins low level of transformation on farming environment
The Competition Commission released its final report on the Fresh Produce Market Inquiry in mid-January, maintaining that transformation in the industry was being impeded by a lack of support for emerging farmers.

Illegal fishing in Australia reveals market gap for farmed sea cucumber
Illegal fishing practices in Australia have revealed a large market opportunity for sea cucumber farming.

An introduction to the Ford Ranger Tremor
In December 2024, the CAR magazine team received the Ford Ranger Tremor to accompany them through the festive season and into the new year. Oliver Keohane looks at what the Tremor is all about.

A farmer's experience with bush encroachment
Farmer David Addenbrooke has worked in the Zimbabwean beef industry for around four decades. Here, he relates his experience with bush encroachment and offers farmers some advice on battling this scourge.
Good rains boost SA's summer grain crop prospects
This week, Absa AgriBusiness analyses several market dynamics and shares its expectations for local grain and oilseed prices over the coming months.
A self-help tool for getting young people engaged in agriculture
The active engagement of the youth in agriculture is pivotal to the sustainability and growth of the sector. Empowering them with the necessary support is key to nurturing future farmers who are equipped to overcome future challenges like the effects of climate change.Dr Primrose Madende, researcher at the Department of Agricultural Economics at the University of the Free State

Rallying to the cackle of this raucous bird
The gregarious and territorial Green Wood-hoopoe, also known as the Red-billed Wood-hoopoe, is extremely vocal and is often heard before it is seen. And for very good reason,

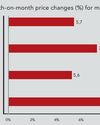
SA coffee lovers can expect price increase
South African coffee prices are expected to spike sharply in the foreseeable future because of failed crops in the country’s main importing countries: Brazil and Vietnam.

Paving the way for a greener dairy industry
The dairy industry is often criticised for its environmental impact, but a new innovation called DESTiny aims to empower farmers to take control of their carbon footprints. Riana Reinecke, the tool's developer, explained to Glenneis Kriel how it works and how farmers can benefit from it.