
Dungeons and Dragons is a complex, fantasy role-playing game, in which various players roll polyhedral dice with 4 to 20 faces to determine outcomes at various decision points. Andrew describes an electronic device he created to simulate rolling the dice using a Raspberry Pi RP2040 MCU, a TFT with touchscreen to show the rolling dice and display the scores from each roll, and an STM amplifier to add the element of drama with sound effects.
My daughter is a big fan of Dungeons and Dragons, the fantasy role-playing game. This game has been around since the 1970s but has become hugely popular during the last few years. One of the key aspects of the game mechanics is the use of polyhedral dice to decide the outcome at various decision points. A typical set of dice, shown in Figure 1, includes seven dice. Six with 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, or 20 faces (designated D4, D6, and so on), along with a second, 10-faced die, the "percent" die. As the name suggests, the "D%" die is used together with the D10 to get a score ranging from 1 to 100 percent; one die gives the tens digit and the other gives the ones digit.
There is sometimes a requirement for a Yes/No decision. This can be done in various ways - for example by using a D6 and designating odd numbers to indicate a No and even numbers a Yes, or by using a special coin-like token. There is frequently the requirement to roll several dice and use the sum of their values to determine game outcomes.
If you look online, you will see that a plethora of beautifully decorated D&D dice sets are available. The die-rolling experience is an integral part of the enjoyment of the game, and the dedicated D&D aficionado will have several sets to choose from.
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

Renesas New RA8 Entry-Line MCU Groups Brings High Performance of Arm Cortex-M85 Processor to Cost-Sensitive Applications with Market-Leading CoreMark Performance
Renesas Electronics Corp., a premier supplier of advanced semiconductor solutions, introduced the RA8E1 and RA8E2 microcontroller (MCU) groups, extending the industry's most powerful series of MCUs.

Same Sky Expands AMT Absolute Encoder Line to Support Larger Shaft Sizes
Same Sky's Motion & Control Group announced the addition of a new series to its innovative AMT absolute encoder family designed to support larger motor shaft sizes from 9mm to 15.875mm (5/8 inch).

XP Power Launches New Series of Low-Profile, Baseplate-Cooled DC-DC Brick Converters
The RDF150 and RDF200 series are the latest additions to the RDF series of low-profile, baseplate-cooled, ultra-wide input DC-DC brick converters, which is already available in power outputs of 25W and 50W.
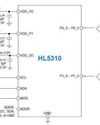
HMI Introduces Ultra-Low Voltage 12-bit GPIO Expander with Interrupt Output
HMI, a leading provider of advanced analog and power management technologies, announced the launch of its HL5310, an innovative ultra-low voltage 12-bit GPIO expander featuring interrupt output.

The Future of Embedded Chip Design Navigating the Chip Creation Space
Custom Silicon at Lower Cost, Reduced Development Time

The Long and Winding Road
From Maxim's RS-232 to WeMos ESP32: So Much to Do, So Little Time

Start to Finish Driving LCDs
Lumex Display with Microchip Driver for a TI MCU

Easing the Path for App Releases
Managed Development of React Native with Expo

Datasheet: Tiny Embedded Boards
Deliver Power, Performance, and Versatility in Meager Square Millimeters

Harvesting Ambient Energy
Hybrid Power Sources Cut IoT Battery Dependency