
Chile's Elqui Valley hides a secret door to the stars. A narrow highway heads east through the region's fertile carpet of green dedicated to producing grapes for both wine and Chile's famous Pisco brandy. I found myself making my way along a dirt road beside one of the region's many vineyards.
After using the proper paperwork to pass through the checkpoint, I traveled along 20 miles of mountain passes to the summit of Cerro Pachón. Here is the Gabriela Mistral Dark Sky Sanctuary, which numbers among the darkest and driest places on Earth.
On a mountain ridge 2,700m above sea level is the new home to one of astronomy's most important new facilities, the Vera C Rubin Observatory. It's been taking shape here since 2015 and, from next year, is set to change astronomy forever.
Rubin Observatory is not alone on the mountainside. A few miles before the ridge is a turn-off to the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, while just beyond it is the 8.1-metre (26.5ft) Gemini South telescope. Beyond that, the 4.1-metre (13.4ft) SOAR (Southern Astrophysical Research) telescope. It's a breathtaking place to be - in more ways than one, thanks to the thin air at such altitude. Even getting out of the car too quickly was enough to make me dizzy. Like another recent arrival, I'd come to take a look around. But while I was here to explore the observatory, this new addition will be the one taking in the night sky above.
Camera as big as a car
In late May this year, the world's largest camera arrived at the Rubin Observatory. The camera has taken a decade to build at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, California. It's about the size of a car and cost $168 million (£132 million), funded by the US Department of Energy's Office of Science.
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

Could We Find Aliens by Looking for Their Solar Panels?- Designed to reflect ultraviolet and infrared, the panels have a unique fingerprint
Researchers searching for life beyond Earth spend a lot of time thinking about what telltale signs might be detectable astronomically. Forms of unambiguous evidence for the presence of life on another world are known as biosignatures. By extension, techno signatures are indicators of activity by intelligent, civilisation-building life.

Antimatter- In our continuing series, Govert Schilling looks at antimatter, the strange counterpart to most of the matter filling our Universe
Particles and corresponding antiparticles are very much alike, except they have opposite electrical charges. For instance, the antiparticle of the electron - known as the positron - has the same tiny mass, but while electrons carry a negative electrical charge, positrons are positively charged.

Where Have All The Milky Way's Early Stars Gone?- Our Galaxy has a curious lack of pristine stars
The Big Bang produced a Universe filled almost exclusively with hydrogen and helium; all other elements - what astronomers call metals - were produced by stars, supernovae and everything that happens later. So if you can pick out a pristine star with no metals polluting it from among the billions in the Milky Way, then you are likely to have a star dating from our Galaxy's earliest days.

Inside The Sky At Night - Two years ago, exoplanet scientist Hannah Wakeford received some of the first data from the JWST
Two years ago, exoplanet scientist Hannah Wakeford received some of the first data from the JWST. In July's Sky at Night, we discovered what she's learned since then.

How to stack DSLR data in Siril
Easily combine multiple frames to boost detailin your astro photos
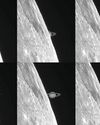
Lunar occultation of Saturn
You'll need to strike a balance on 21 August to capture the Moon covering the ringed planet
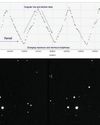
How to plot a variable star light curve
A rewarding project to chart stars that change brightness

Smartphone photography with a telescope
Mary Mcintyre explains how to get impressive night-sky images using your phone

Once-a-century solar storm is overdue
If a Carrington Event struck today it would be catastrophic, says Minna Palmroth

The new era of human spaceflight
There's been a step-change in crewed space missions since the dawn of the 21st century. Ben Evans charts its course and looks ahead to future horizons