
Dante Lauretta sat in the backseat of a helicopter hovering high above a remote patch of Utah desert, waiting for a small, twinkling speck in the sky to plunge toward earth.
If you didn't know better, you might think what was beginning to burn through the skies above the American southwest in the early hours of September 24, 2023, was a shooting star. But it wasn't a shooting star. Or a meteor. It was a dishwasher-size capsule filled with bits of ancient asteroid-priceless matter from the dawn of the solar system. In other words, it was a treasure chest moving at 27,000 miles per hour and sizzling at a temperature half that of the sun's surface.
That small streak of light represented the end of a NASA-led interplanetary mission suffused with peril. Lauretta and his colleagues had spent nearly 20 years building a spacecraft designed to collect material from an asteroid and return to Earth. From these precious grains, they hoped to gain insight about the formation of the solar system, of Earth, and maybe even of life itself.
What the capsule had to do now, completely autonomously, was simple: stay in one piece as it reentered the atmosphere, open its parachutes, and softly touch down on an Air Force bombing range without detonating any unexploded ordnance nearby.
By 8:44 a.m., the capsule was 102,300 feet above the ground, and its drogue parachute-the canopy meant to stabilize its plunge-should have opened by now. But no one could see it. Throngs of scientists and engineers who had worked on the spacecraft, spread out across mission control rooms in Arizona and Colorado, were now deathly quiet.
It looked like something had gone wrong. And all Lauretta, the mission's leader, could do was watch, and hope, that his life's obsession wasn't about to be scattered across the desert. He wasn't even supposed to oversee the mission.
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

ONE OF THE 'GREATEST THREATS' TO THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST ISN'T WHAT YOU THINK.
EXPERTS ARE PREPARING THE REGION AGAINST THE THREAT OF DANGEROUS VOLCANIC MUDFLOWS, KNOWN AS LAHARS, WHICH COULD INUNDATE THE COMMUNITIES SURROUNDING MT. RAINIER IN AS LITTLE AS 30 MINUTES.

THE WORLD'S TOUGHEST ROW
They rowed 3,000 miles across the Atlantic, battling unpredictable weather, chaotic seas, and finicky equipment. But what they discovered gave them profound new insights into the power of the ocean.

HOW TO DIY OFF-GRID SOLAR
SPEND THE TIME UP FRONT AND PLAN IT CAREFULLY TO AVOID DISAPPOINTMENT
Are We on the Verge of an ARMS RACE in SPACE?
RUMORS OF A RUSSIAN SPACE NUKE, ALONG WITH OTHER SATELLITE-TARGETING WEAPONS, HAVE MADE GEOPOLITICAL TENSIONS EXTEND INTO ORBIT.

Fresh Fingerprints on an Ancient Statue
A CLAY FIGURINE HAS SPENT MILLENNIA incomplete, waiting at the bottom of a lake for its long-dead craftsman to finish the Iron Age-era statuette.

Quantum Entanglement in Our Brains
IT HAS LONG BEEN ARGUED THAT THE human brain is similar to a computer. But in reality, that's selling the brain pretty short.

The Tools of Copernicus
WAY BACK IN 1508, WITH ONLY LIMited tools at his disposal, Nicolaus Copernicus developed a celestial model of a heliocentric planetary system, which he described in hist landmark work De revolutionibus orbium coelestium. It was a complete overhaul of our conception of the universe-one that, unfortunately, earned him the ire of the Catholic church for decades after his death-and forever changed the way we look at the stars.

Building a Sixth-Generation Bomber Raptor
THE GLOBAL COMBAT AIR Programme (GCAP)-a project by the U.K., Italy, and Japan to develop a sixth-generation stealth fighter-has been busy at the drawing board reshaping its vision of the future of air warfare. And judging by the new concept model unveiled at this year's Farnborough air show, that future has big triangular wings.

The Electroweak Force of the Early Universe
TODAY, THE UNIVERSE AS WE KNOW IT IS governed by four fundamental forces: the strong nuclear force, the weak nuclear force, electromagnetism, and gravity.
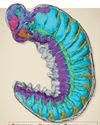
This Ancient Fossil With a Brain and Guts
WE KNOW WHAT FOSSILS LOOK like. For example, typical dinosaur fossils are bones turned to stone and preserved from the passage of time, located, if we're particularly lucky, in large collections that can be reassembled to represent the beast they used to prop up in their entirety.