
Green hydrogen (GH) is attracting worldwide attention and emerging as the most promising solution for a cleaner, greener, and sustainable future. Depending on the method used for the production, hydrogen is categorised into three types, grey, blue, and green—as shown in Fig. 1. Grey hydrogen is produced using fossil fuels such as natural gas or coal. The processes that are used, the steam methane reforming and the coal gasification, release a significant amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. Grey hydrogen is the cheapest and most used form and accounts for about 95% of the hydrogen produced in the world. Blue hydrogen is produced using the same methods as used for the grey hydrogen, except that most of the CO2 produced is sequestered (stored in the ground) using the carbon capture and storage (CCS) methodology. Capturing and storing the CO2 emissions, instead of releasing them into the atmosphere, makes the blue hydrogen a lower-carbon fuel as compared to the grey hydrogen.
GH on the other hand is produced by the electrolysis of water using the clean renewable energy produced by sources such as wind and solar. The process emits only water vapour, leaving no residue in the air, which makes GH the cleanest energy source.
GH, presently, has a low share in the global energy market since it is very expensive to produce. Efforts are being made to reduce the costs. As per the estimate of International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), an 80% drop in cost is possible by the year 2030, provided the cost of electrolysers is reduced and the renewable energy cost dips below US$20/MWh.
PROCESSES USED TO PRODUCE GREEN HYDROGEN
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

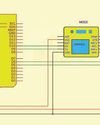
STK435 IC-Based STEREO AMPLIFIER
This stereo AF amplifier uses the STK435 IC, a highly popular choice due to its simplicity.
A SEWER DRAIN SHIELD For Smart Cities
Drainage systems are vital for storm water management but often transport pollutants, especially plastics, to rivers and oceans, harming ecosystems.

ESP32 SPEECH FUNCTION: Text To Speech
Speech capability in technology primarily has two dimensions: text to speech (TTS) and speech to text (STT). This device focuses on TTS.

World's Smallest Programable INDUSPHONE DESIGN
This is the second part of designing the world’s smallest phone, where the UI is integrated with the basic functions of the phone.

FLAME-SENSING FIRE ALARM Using An Arduino Nano
Fire safety alarms are crucial in both residential and industrial environments.

loT-Based Distribution Transformer CONDITION MONITORING SYSTEM
The proposed IoT-based distribution transformer condition monitoring system enables real-time monitoring of distribution transformers, identifying such deviations as overload conditions and overheating.

Wi-Fi 6 AND Wi-Fi 7 Powering The Next Wave of Smart Connectivity
Wi-Fi 6 leads with faster data rates and reduced latency while upcoming Wi-Fi 7's backward compatibility will facilitate gradual upgrades from Wi-Fi 6, easing transitions. However, advanced features like multi-link operation (MLO) and ultra-low latency may command a premium, making Wi-Fi 7 suited for high-end applications.

CHARGE FORWARD: High-Voltage Batteries And MSMEs Can Fuel INDIA'S EV REVOLUTION
A nuanced explanation of low- and high-voltage EV batteries by Dr Gokhale, Vice President for Battery Technology at JSW Energy, illuminates their advancements and influence. The essential role of MSMEs and academia in developing a strong EV ecosystem emerges, marking their significance for India's push towards self-reliance in this innovative field.

"MILES TO GO Before I Sleep"
A teacher illuminates the path to success through the light of knowledge, yet some teachers extend that light to society through their contributions and research. Known as the architect of the modern M3 electronic voting machine (EVM) and the voter verifiable paper audit trail (VVPAT) that transformed India's democratic process, Prof. (Dr) Rajat Moona's journey began in the modest town of Bareilly. Here is his story, as recounted to and written by EFY's Yashasvini Razdan.

STARTUPS & INNOVATORS
1 One Charger To Charge All Your Devices | 2 Harnessing AI Technology For Efficient Pest Management | 3 Wireless Light-Based Communication With Velmenni's Technology