
Sometimes, computerised Go-To telescopes aren't all they're cracked up to be. Yes, they can automatically slew to an object in the night sky that otherwise a beginner would struggle to find, but such motorised scopes still need to be aligned with bright stars. For beginners, whose only way of navigating the night sky is by using a smartphone app, that can be tricky. So why not just use that app to align the telescope? That's the thinking behind Celestron's StarSense technology, which provides a free app and a carefully designed adaptor to fuse old and new techniques and create a novel way of exploring the night sky.
The DX 130AZ is a 5.1-inch (130mm) Newtonian reflector telescope that has a focal length of 650mm, giving a focal ratio of f/5, while the tube is 630mm long. It's mounted on a manual altaz 'Push-To' black aluminium tripod that proves this telescope's weak point. It's steady enough for the job once the spreader accessory tray is in place, but only just, and we did experience some vibrations after each movement. Since there's no motorised tracking mount, astrophotography is out of the question, save for a spot of afocal photography through the eyepiece. That, of course, requires a smartphone, which isn't going to be possible if you use this telescope as the maker intended you to (unless you have a spare phone). Although it's not essential to make the telescope usable, Celestron's StarSense Explorer app is at the core of how this combination works.
Upgrades
Also included with the DX 130AZ are two 1.25-inch eyepieces, 25mm and 10mm, which give 26x and 65x power, respectively. The supplied low-power eyepieces are nothing special and could easily be upgraded (a Barlow lens being the most obvious candidate), but they'll serve beginners well. A red dot finder is also provided if you want to ignore the app and aim the DX 130AZ completely manually.
この記事は BBC Sky at Night Magazine の July 2022 版に掲載されています。
7 日間の Magzter GOLD 無料トライアルを開始して、何千もの厳選されたプレミアム ストーリー、9,000 以上の雑誌や新聞にアクセスしてください。
すでに購読者です ? サインイン
この記事は BBC Sky at Night Magazine の July 2022 版に掲載されています。
7 日間の Magzter GOLD 無料トライアルを開始して、何千もの厳選されたプレミアム ストーリー、9,000 以上の雑誌や新聞にアクセスしてください。
すでに購読者です? サインイン

Could We Find Aliens by Looking for Their Solar Panels?- Designed to reflect ultraviolet and infrared, the panels have a unique fingerprint
Researchers searching for life beyond Earth spend a lot of time thinking about what telltale signs might be detectable astronomically. Forms of unambiguous evidence for the presence of life on another world are known as biosignatures. By extension, techno signatures are indicators of activity by intelligent, civilisation-building life.

Antimatter- In our continuing series, Govert Schilling looks at antimatter, the strange counterpart to most of the matter filling our Universe
Particles and corresponding antiparticles are very much alike, except they have opposite electrical charges. For instance, the antiparticle of the electron - known as the positron - has the same tiny mass, but while electrons carry a negative electrical charge, positrons are positively charged.

Where Have All The Milky Way's Early Stars Gone?- Our Galaxy has a curious lack of pristine stars
The Big Bang produced a Universe filled almost exclusively with hydrogen and helium; all other elements - what astronomers call metals - were produced by stars, supernovae and everything that happens later. So if you can pick out a pristine star with no metals polluting it from among the billions in the Milky Way, then you are likely to have a star dating from our Galaxy's earliest days.

Inside The Sky At Night - Two years ago, exoplanet scientist Hannah Wakeford received some of the first data from the JWST
Two years ago, exoplanet scientist Hannah Wakeford received some of the first data from the JWST. In July's Sky at Night, we discovered what she's learned since then.

How to stack DSLR data in Siril
Easily combine multiple frames to boost detailin your astro photos
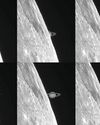
Lunar occultation of Saturn
You'll need to strike a balance on 21 August to capture the Moon covering the ringed planet
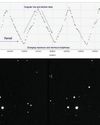
How to plot a variable star light curve
A rewarding project to chart stars that change brightness

Smartphone photography with a telescope
Mary Mcintyre explains how to get impressive night-sky images using your phone

Once-a-century solar storm is overdue
If a Carrington Event struck today it would be catastrophic, says Minna Palmroth

The new era of human spaceflight
There's been a step-change in crewed space missions since the dawn of the 21st century. Ben Evans charts its course and looks ahead to future horizons