
Microplastics are all over the news lately. Actually, these plastic bits 0.2 inches (5 mm) wide or smaller are all over everything— from our food to the insides of animals, and especially in the oceans.
Most plastic is non-biodegradable. When something biodegradable breaks down, it chemically changes into new substances. Bacteria and other microbes will digest a banana peel over a few weeks until it becomes soil. By contrast, plastic stays plastic forever. But it can still physically break into smaller pieces. This happens fastest outside, because the ultraviolet light in sunlight weakens and cracks plastic. Eventually, it breaks into smaller pieces. There’s no limit to how small those pieces can get, and that’s how we end up with microplastics. Bigger microplastics might look like individual grains of dust, just barely big enough to see with your eyes. Others are invisible without a microscope. These may be the size of human blood cells, or even around 10 times smaller than that, which is the size of some viruses!
So why all the attention? Microplastics are a newly discovered pollutant, and scientists around the world are worried that they can hurt animals and spread chemical pollutants around.
Problems for Animals Periodically, big sea animals like turtles or whales accidentally eat plastic debris. Similarly, very small animals in the ocean called zooplankton sometimes eat microplastics. To them, a piece of plastic might smell and taste good, because chemicals that smell like their normal food form on the surface of microplastics. But these critters can’t digest plastic, so one of two things happens. Hopefully, the plastic goes right through the zooplankton unchanged and, ahem, comes out the other end. But if a jagged piece of plastic gets stuck inside their guts, it can hurt or even kill them.
Denne historien er fra September 2019-utgaven av Muse Science Magazine for Kids.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent ? Logg på
Denne historien er fra September 2019-utgaven av Muse Science Magazine for Kids.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent? Logg på

A 12-Year-Old Girl's Election Sticker Is a Winner
VOTING IS A FUNDAMENTAL FREEDOM FOR AMERICANS, A MEANS OF DOING ONE'S CIVIC DUTY AND A WAY AN INDIVIDUAL CAN EXPRESS THEIR VOICE. In 1971, the United States lowered its voting age to 18. But that doesn't mean kids and teens under 18 can't participate in elections in various ways.
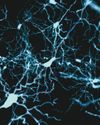
If everything the human brain does is basically sets of electrical impulses, how exactly does that translate into a state of mind?
You're not the only one asking this question. Every neuroscientist in the world is wondering the exact same thing, says Zach Mainen

EARTH'S TINIEST BUILDERS
THE HIDDEN WORLD OF MICROBES IN THE EARTH'S CRUST

MUMMIES SPEAK
ABOUT MICROBES, MIGRATION, AND MORE

GOING WITH YOUR GUT
HOW DO MICROBES AFFECT OUR HEALTH? LET'S COUNT THE WAYS...

BUG Detective
A burglar sneaks into a house on a quiet street in New York City. He walks through the house, touching countertops and door handles. Finally, he steals a single card from a full deck. Then he leaves.

Little Creatures Among Us THE MANY MICROBES IN OUR DAILY LIVES
When you think you're alone, you're actually not. In the ground, the air, your room, and even your body are Strillions and trillions of creatures so tiny you can't see them.

A Mars Rock Found With Leopard Spots Could Be a Sign of Ancient Life
IN JULY, NASA'S PERSEVERANCE ROVER CAME ACROSS A SPOTTED ROCK IN WHAT WAS ONCE A RIVERBED IN THE JEZERO CRATER ON MARS.

Para Athlete Uses Exoskeleton Suit to Carry the Olympic Torch
In July, a 36-year-old French tennis para athlete, Kevin Piette, got a chance to participate in this summer’s Olympic torch relay without using a wheelchair.

Ancient Egyptians May Have Used a Water System to Lift Stones to Build Pyramid
HOW ANCIENT EGYPTIANS BUILT THE MASSIVE PYRAMIDS IN EGYPT MORE THAN 4,000 YEARS AGO HAS LONG BEEN A TOPIC OF WONDER AND DEBATE.