
At last, the mystery at the heart of our Milky Way Galaxy has been uncovered. On 12 May at 13:07 UT, the first-ever direct visual image of our closest supermassive black hole was unveiled by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) team. It was a thrilling, profound moment.
Though not the first black hole picture presented by the EHT collaboration - that accolade belongs to M87* first presented in April 2019 - it was one long sought after. As nothing, not even light, can escape beyond a black hole's event horizon, they are impossible to see directly. Instead, for decades, astronomers have attempted to track it down by looking for giant stars circling an otherwise invisible point in space. Now we have its image or, more accurately, its silhouette. Our Galaxy's 'central engine' exists.
Over five nights in April 2017, astronomers observed Sgr A* (pronounced "sadge-ay-star") in the constellation of Sagittarius with eight radio telescopes, at six sites from Arizona to the South Pole and Spain to Hawaii. Part of the EHT collaboration - a global network of synchronized radio dishes yielding an Earth-sized virtual telescope of planet-wide aperture - it was the result of decades of work involving more than 300 people and 80 institutions. Using the technique of very long baseline interferometry, the EHT offered the highest possible resolving power from the surface of Earth, capturing objects as small as 20 micro-arcseconds on the sky - that's equivalent to spying a doughnut on the Moon.
Denne historien er fra July 2022-utgaven av BBC Sky at Night Magazine.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent ? Logg på
Denne historien er fra July 2022-utgaven av BBC Sky at Night Magazine.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent? Logg på

Could We Find Aliens by Looking for Their Solar Panels?- Designed to reflect ultraviolet and infrared, the panels have a unique fingerprint
Researchers searching for life beyond Earth spend a lot of time thinking about what telltale signs might be detectable astronomically. Forms of unambiguous evidence for the presence of life on another world are known as biosignatures. By extension, techno signatures are indicators of activity by intelligent, civilisation-building life.

Antimatter- In our continuing series, Govert Schilling looks at antimatter, the strange counterpart to most of the matter filling our Universe
Particles and corresponding antiparticles are very much alike, except they have opposite electrical charges. For instance, the antiparticle of the electron - known as the positron - has the same tiny mass, but while electrons carry a negative electrical charge, positrons are positively charged.

Where Have All The Milky Way's Early Stars Gone?- Our Galaxy has a curious lack of pristine stars
The Big Bang produced a Universe filled almost exclusively with hydrogen and helium; all other elements - what astronomers call metals - were produced by stars, supernovae and everything that happens later. So if you can pick out a pristine star with no metals polluting it from among the billions in the Milky Way, then you are likely to have a star dating from our Galaxy's earliest days.

Inside The Sky At Night - Two years ago, exoplanet scientist Hannah Wakeford received some of the first data from the JWST
Two years ago, exoplanet scientist Hannah Wakeford received some of the first data from the JWST. In July's Sky at Night, we discovered what she's learned since then.

How to stack DSLR data in Siril
Easily combine multiple frames to boost detailin your astro photos
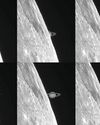
Lunar occultation of Saturn
You'll need to strike a balance on 21 August to capture the Moon covering the ringed planet
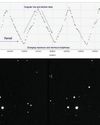
How to plot a variable star light curve
A rewarding project to chart stars that change brightness

Smartphone photography with a telescope
Mary Mcintyre explains how to get impressive night-sky images using your phone

Once-a-century solar storm is overdue
If a Carrington Event struck today it would be catastrophic, says Minna Palmroth

The new era of human spaceflight
There's been a step-change in crewed space missions since the dawn of the 21st century. Ben Evans charts its course and looks ahead to future horizons