Someone with imagination and the right kind of boat. In 1842, James B. Eads proved that he had both the imagination and the know-how to design such a boat.
Eads was born in 1820 in Indiana. His family moved around a lot as his father tried to earn a living. When the Eads family moved to St. Louis, Missouri, in 1833, James stopped attending school and found jobs to help support his family. In his free time, he read books about civil engineering and machinery. By the time he was 19, he had a job as a cargo clerk on the Knickerbocker, a river steamboat.
An accident on the steamboat got Eads thinking about salvage. He started with a flat-decked barge holding a derrick. A 40-gallon wooden barrel served as a makeshift diving bell. Lowered into the Mississippi River by the derrick, the diving bell allowed Eads to walk on the river's bottom. He spent hundreds of hours exploring. He observed that where the river ran fast, it scoured and deepened its channel. Where the river slowed, it deposited sediment that collected into sandbars.
By 1856, Eads was the respected captain of a fleet of salvage boats on the river. And his firsthand knowledge of the river became invaluable to him as he created monumental works of engineering that forever altered the Mississippi.
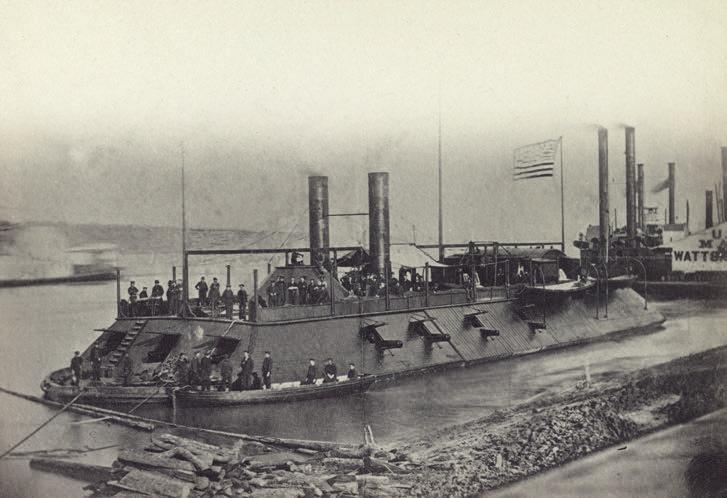
But the Civil War (1861-1865) initially put such projects on hold. The federal government asked Eads to build river gunboats for the Union. Eads built more than 30 ironclads, constantly incorporating improvements. The ironclads helped the Union win important victories on the Mississippi River and along the Gulf of Mexico.
Denne historien er fra April 2023-utgaven av Cobblestone American History Magazine for Kids.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent ? Logg på
Denne historien er fra April 2023-utgaven av Cobblestone American History Magazine for Kids.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent? Logg på

Eye in the Sky
An interview with Joe Piotrowski

Airborne Animals
Humans have taken to the skies in balloons, gliders, and airplanes-but we're not alone among the clouds. Animals of all sorts have evolved to harness wind power.

TAKING OFF
The Wright brothers expected airplanes to “take off,” but even they might be amazed at the way the airline industry has become big business. In the past, it was expensive to send something by plane.

GROWTH OF AN INDUSTRY
After their historic flight at Kitty Hawk in 1903, Wilbur and Orville Wright returned to Dayton, Ohio. They spent the next few years making adjustments and building additional versions of their powered aircraft in their bicycle shop.

WHY KITTY HAWK?
The Wright brothers searched carefully for the best place to test their gliders and flying machines. Their main concern was for good, steady winds. But they also hoped to find a remote location to allow them to perform tests away from the public eye.

Two Brothers From Ohio
Most people do not realize that the Wright brothers—Wilbur, born in 1867, and Orville, born in 1871—performed various scientific experiments before inventing their aircraft. For as long as anyone in their hometown of Dayton, Ohio, could remember, the Wright boys had worked on mechanical projects.

A Helping Hand
May 6, 1896. A group of people who had gathered beside the Potomac River, just south of the U.S. capital, grew quiet. Then, it erupted in cheers as a small, unmanned aircraft took to the skies and flew for more than half a mile. The flight came seven years before the Wright brothers’ first manned, powered flight. The inventor of the aircraft was Dr. Samuel Pierpont Langley.

THE IDEA MEN
People dreamed of flying thousands of years before the Wright brothers found success near Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. These dreamers, such as Leonardo da Vinci, studied birds flying and imagined how humans might do the same—if only they had wings. Other men developed a more hands-on approach to the topic. Early inventors made wings of cloth, glue, and feathers and tied these creations to their arms in an attempt to imitate nature.

Da Vinci's 4 Designs
Have you ever wondered how a bird flies? Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) did. He thought that understanding how a bird flies would provide the key to human flight. So, what did da Vinci learn from birds?

Silken Wings
Seven hundred years before the Wright brothers began experimenting with human flight, the Chinese had already mastered its secrets—with kites.