
We used to think of Earth and the night sky as completely different realms. Whereas Earth is lush, green and filled with life, outer space is remote, dark and forbidding. Now we know that is simply not true.
Instead of outer space, we should think of it as near space. As British astronomer Fred Hoyle (1915-2001) was quoted as saying in a 1979 edition of The Observer: "Space isn't remote at all. It's only an hour's drive away if your car could go straight upwards."
Our use of satellites for communications, navigation and observation has tied Earth and space together as never before. It's no exaggeration to say that society as we know it could not function without the satellite networks that circle the planet.
Something approaching half of the 195 countries in the world now own at least one satellite. As a result, what happens in space inevitably influences what happens on Earth, and vice versa. Space has become an extension of Earth's environment, a new frontier where human influence is felt.
It's therefore essential that we understand the limits of this new environment and its resources to ensure that our current activities are sustainable, so that future generations can continue to benefit from the unique opportunities that space offers.
A CHANGE OF APPROACH
"I do think we're at a juncture where we need to review what we've been doing in space and consider what's needed for the future," says Joanne Wheeler, managing partner at the London-based law firm Alden Legal, which specialises in satellite, space and communications law.
Wheeler has a background in space law and international environmental law, and has been interested in space debris for around 25 years, having once been the European Space Agency's main lawyer covering issues related to space debris.
Denne historien er fra August 2023-utgaven av BBC Science Focus.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent ? Logg på
Denne historien er fra August 2023-utgaven av BBC Science Focus.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent? Logg på

THE WORST IDEAS OF THE 21ST CENTURY
NOT ALL IDEAS CAN BE HITS. ALONGSIDE GROUND-BREAKING INNOVATIONS, 21ST-CENTURY SCIENTISTS HAVE HELMED THEIR SHARE OF WILD TECH FLOPS, DUBIOUS THEORIES AND OVERHYPED BREAKTHROUGHS. HERE ARE THE BIGGEST TO FORGET

10 IDEAS THAT WILL SHAPE YOUR NEXT 25 YEARS
Predicting the future is considered a fool's game. But it's one many of us like to play.

THE BIGGEST BREAKTHROUGHS OF THE CENTURY
We're a quarter of the way into the new century. To mark this milestone, we asked the UK's top minds to highlight some of the game-changing scientific breakthroughs shaping our world since the year 2000

DO THE SCIENCE COGNITIVE SHUFFLE
Trouble sleeping? A lot on your mind? Use this trick and sedate your synapses
WHAT DETERMINES HOW MANY ABS I CAN GET?
Assuming you're a human being, you have exactly the same number of abs as everybody else: two.

HOW CAN I IDENTIFY MY PSYCHOLOGICAL BLIND SPOT?
In the 1950s two American psychologists, Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham, proposed a way of thinking about psychological blind spots - things you don't know about yourself - that they called the 'Johari Window' (the term is a combination of their first names).

How can I change my personality?
Want to become more confident, extroverted or assertive? Science shows that with a few simple changes, you can unlock your best self

Could your cosmetics be harming your health?
Cosmetic companies are phasing out microplastics and so-called 'forever chemicals' to help protect consumers.

extraterrestrial US Congress is talking about activity again. Is the truth really out there?
Despite several testimonies, the question remains frustratingly unanswered
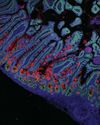
Map of 100 million human body cells revealed
Over three dozen new studies mark significant milestone towards complete Human Cell Atlas