
As you read this, five of the eight planets in the Solar System have spacecraft orbiting them or landers on their surfaces - and more are on the way. In his new series Solar System, Prof Brian Cox reveals the freshest insights coming from these spacecraft and landers, and which of the planets they're studying holds the most promise for finding signs of life.
So, naturally, we had to ask him all about it: from filming in the most alien-like places on Earth to his hope that aliens might explore the vast expanses of the Universe after we humans (possibly) extinguish ourselves.
As a show, Solar System sounds familiar, but this series is very current and looks behind the scenes of the biggest space missions right now. What were your hopes for the show?
That was one of the central ones: to show that there are over 40 spacecraft currently active in the Solar System, so the amount of knowledge that we have of our neighbourhood is increasing all the time. With that increase - that huge amount of data that's raining down on us every second from these probes - we find that there are more questions than answers quite a lot of the time.
So, as with a lot of science, one of the things I hope that the audience takes away is that in no sense do we know everything about our neighbourhood in space.
In particular, [in the show] we talk about life - and life is a central part of any exploration of the Solar System. We say that the Solar System is a giant chemistry set and life is chemistry complex carbon chemistry.
I think it's fair to say that we're finding more potential habitats than we ever would have guessed, in stranger places than we ever would have guessed. Ceres, the minor planet, is a good example. The fact that it appears, because of data from a spacecraft called Dawn, to have liquid water below its surface is a tremendous surprise.
Denne historien er fra October 2024-utgaven av BBC Science Focus.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent ? Logg på
Denne historien er fra October 2024-utgaven av BBC Science Focus.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent? Logg på

THE WORST IDEAS OF THE 21ST CENTURY
NOT ALL IDEAS CAN BE HITS. ALONGSIDE GROUND-BREAKING INNOVATIONS, 21ST-CENTURY SCIENTISTS HAVE HELMED THEIR SHARE OF WILD TECH FLOPS, DUBIOUS THEORIES AND OVERHYPED BREAKTHROUGHS. HERE ARE THE BIGGEST TO FORGET

10 IDEAS THAT WILL SHAPE YOUR NEXT 25 YEARS
Predicting the future is considered a fool's game. But it's one many of us like to play.

THE BIGGEST BREAKTHROUGHS OF THE CENTURY
We're a quarter of the way into the new century. To mark this milestone, we asked the UK's top minds to highlight some of the game-changing scientific breakthroughs shaping our world since the year 2000

DO THE SCIENCE COGNITIVE SHUFFLE
Trouble sleeping? A lot on your mind? Use this trick and sedate your synapses
WHAT DETERMINES HOW MANY ABS I CAN GET?
Assuming you're a human being, you have exactly the same number of abs as everybody else: two.

HOW CAN I IDENTIFY MY PSYCHOLOGICAL BLIND SPOT?
In the 1950s two American psychologists, Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham, proposed a way of thinking about psychological blind spots - things you don't know about yourself - that they called the 'Johari Window' (the term is a combination of their first names).

How can I change my personality?
Want to become more confident, extroverted or assertive? Science shows that with a few simple changes, you can unlock your best self

Could your cosmetics be harming your health?
Cosmetic companies are phasing out microplastics and so-called 'forever chemicals' to help protect consumers.

extraterrestrial US Congress is talking about activity again. Is the truth really out there?
Despite several testimonies, the question remains frustratingly unanswered
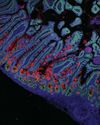
Map of 100 million human body cells revealed
Over three dozen new studies mark significant milestone towards complete Human Cell Atlas