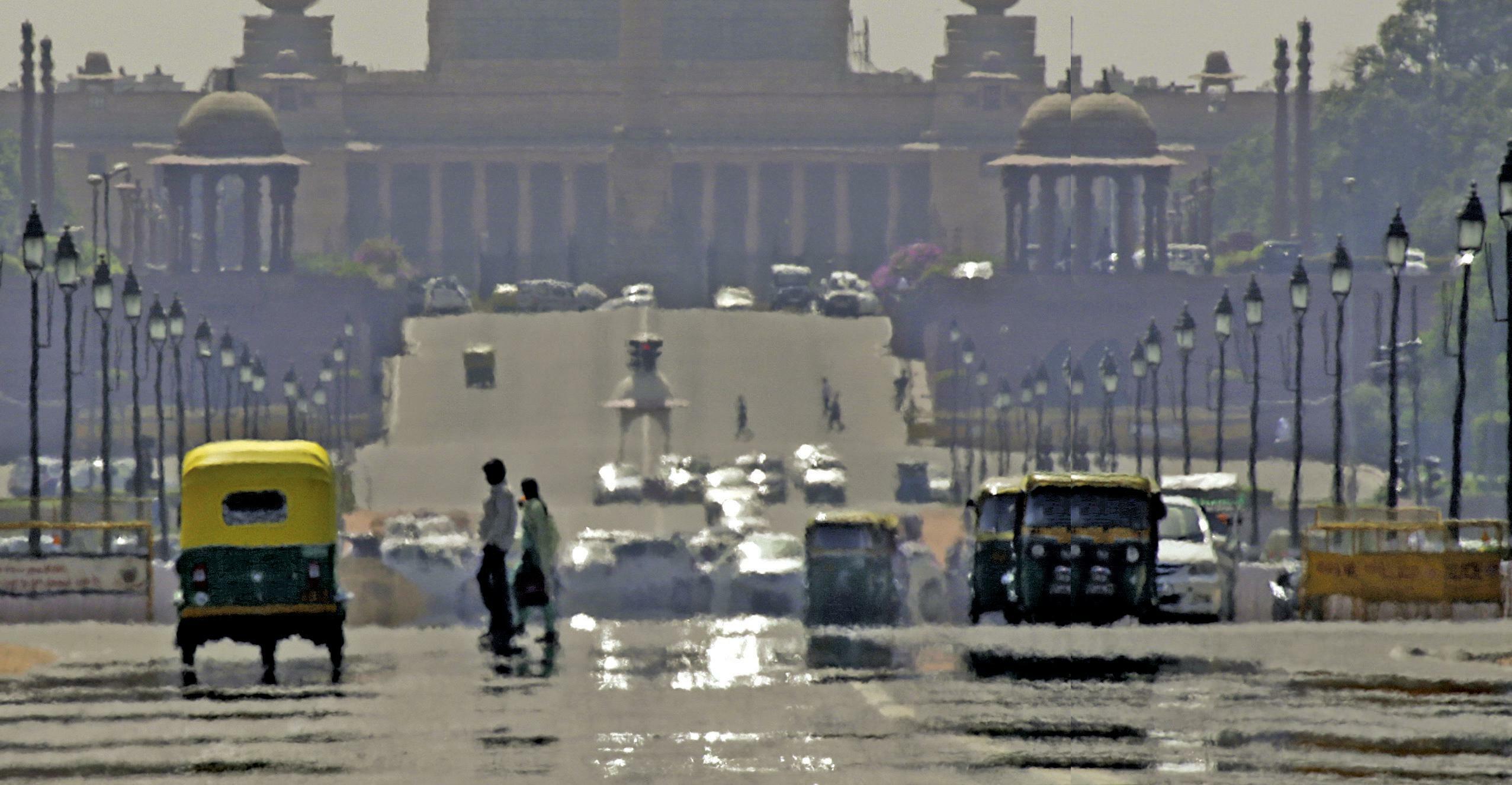

IN A warming world, urbanisation has a profound impact on heat. As a city's population grows, infrastructure needs to be developed to cater to its requirements.
Cities contribute more than two-thirds of global carbon dioxide emissions, according the UN Environment Programme. However, their environmental impact goes beyond emissions. As a city grows, the way buildings, roads and railways are laid out; the density, height and size of buildings, and the materials used; the amount of green spaces and water bodies; and level of human activities such as use of vehicles and airconditioners together determine how much heat is retained in the immediate area.
When released, this heat raises the temperatures of the nearby atmosphere. As the grey infrastructure gets denser and more concentrated, it erodes the natural spaces that act as heat sinks and keep the environment cool (see 'Influencing factors'). If left unchecked, such development could create an urban heat island effect, with cities recording high temperatures that can adversely impact the health of people, and also potentially be fatal.
To analyse the status of urban heat islands in the country and establish the ongoing heat burden that is a result of their development, Delhi-based think tank Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) conducted a study in nine cities-Delhi, Jaipur, Kolkata, Nagpur, Pune, Ahmedabad, Hyderabad, Chennai and Bhubaneswar.
These cities, which are of different sizes and are located in different climatic zones, show that the problem of heat is not restricted to a specific kind of climate or geography.
Denne historien er fra May 01, 2024-utgaven av Down To Earth.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent ? Logg på
Denne historien er fra May 01, 2024-utgaven av Down To Earth.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent? Logg på

CLIMATE SHAPES SPECIES
Gradual changes in a population that lives in a region with environmental shifts give rise to new species

LEAFY GOODNESS
Leaves of the bottle gourd can be a healthy green addition to the plate

'Story of human origin is still not figured out or over'
Fifty years ago, the discovery of a partial skeleton amid the barren desert landscape of northern Ethiopia transformed our understanding of where humans came from, and how we developed into Homo sapiens. \"Lucy\" was first spotted on November 24, 1974, by the American paleoanthropologist Donald Johanson and his student assistant Tom Gray. Named after the Beatles' Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds, a popular song in the their team's camp at the time, it was immediately clear she was a female, because of her small adult size, and that she had walked upright, unlike chimpanzees. Lucy was also very old-at almost 3.2 million years, she was anointed as the then-earliest known (distant) ancestor of modern humans. Over the following decades, rather fittingly given her name, she became a \"paleo-rock star\", going on a US tour from 2006 following a deal with the Ethiopian authorities.

Deadly discharge
Residents of an industrial cluster blame effluent and sewage treatment plants for discharging poorly treated water that contaminates the area, causes skin diseases

US drug regulator faces Trump heat
FAILED REPUBLICAN presidential candidate Vivek Ramaswamy is making more news now than during his doomed attempt to get the party nomination for president. Ramaswamy's decision to throw in the towel and back Donald Trump after his campaign went nowhere showed acumen, the kind he is famous for in the investment world.

Distorted picture
India's groundwater recovery may be misleading, as new assessment methods inflate annual recharge figures and discontinue on-ground verification
A MAKE OR BREAK YEAR
Expect some stiff targets, radical policy measures and rapid innovations as polycrisis reaches a crescendo this year

Commons in crisis
A landmark 2011 Supreme Court ruling to protect shared resources deepens struggles for India's marginalised communities

Europe faces Russian natural gas supply cuts
UKRAINE'S PRIME Minister Denys Shmyhal said on December 16, 2024, that its gas transit agreement with Russia will expire on January 1, 2025, and will not be renewed. The agreement was to allow transit of natural gas to Europe amid the RussiaUkraine conflict.

Preserving a voice
Non-profit in Madhya Pradesh documents Korku language, makes education accessible for the tribal community