
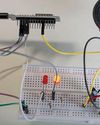
Circuit and working Fig. 2 displays the circuit diagram of the standalone shock and vibration sensor device. It is built around transistor 2N2222 (T1), two electrolytic capacitors: one of 10μF, 16V rating (C1) and the other of 4.7μF, 16V rating (C2), two resistors: one of 330 ohm (R1) and the other of 3.3-kilo-ohm (R2), a yellow LED, and a few other components.
As depicted in Fig. 2, a 3V coin cell (CR2032) is used to power the circuit. The yellow LED (LED1) is triggered by the SW18015P vibration sensor switch through a simple setup comprising the two capacitors, two resistors, and a transistor.
The key to the device is the SW18015P vibration sensor switch, which features a soft spring coiled around a long metal pin, as shown in Fig. 3. When the switch is bumped (from the side only), the spring attached to the first pin touches the centre pole to contact the second pin. During a bump, the two pins act as a closed switch for a brief period.
The short impulses generated by the sensor are processed by the rest of the circuit into reasonably long pulses. Hence, the system emits brief flashes of yellow light when shock or vibration is sensed.
Denne historien er fra December 2024-utgaven av Electronics For You.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent ? Logg på
Denne historien er fra December 2024-utgaven av Electronics For You.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent? Logg på
ESP32-Powered AUDIO-VISUAL SIREN
This sound alternator is designed to simulate the effects of a police siren, combining sound and light to create a dynamic audio-visual experience.

BLDC MOTOR With Web-Based Speed Control Using ESP32
Integrating wireless control into brushless direct current (BLDC) motor systems opens up exciting possibilities for applications such as remote-controlled cars, robots, and other innovative systems.

Pi Zero Portable BILINGUAL TRANSLATOR
This system is designed as a bilingual translator, leveraging the gTTS library to support multiple Indian languages, including English (en), Bengali (bn), Gujarati (gu), Hindi (hi), Kannada (kn), Malayalam (ml), Marathi (mr), Tamil (ta), Telugu (te), and Urdu (ur).

Op-Amp-Based VEHICLE THEFT DETECTOR
A simple, low-cost device can effectively alert homeowners or occupants if a parked vehicle is moved or tampered with.

loT SMART METER With Dashboard
Energy meters in homes track electricity usage, enabling accurate billing by governments and providers.

Choose The Right Cloud Platform For Implementing loT PROTOCOLS
Working with loT protocols like MQTT, AMQP, and CoAP on cloud platforms is essential for developing scalable and efficient lol applications. The choice of the programming platform will depend on factors like project requirements, existing skills, and target devices. Leveraging the appropriate libraries and cloud services can enable seamless integration of lol devices with cloud-based applications.

Why TMR SENSORS Lead Next-Generation Design
TMR sensors are gaining traction in industries needing precision and power efficiency. What makes them the go-to choice for modern designs?

DESIGNING PCBs For EMI Management
Electromagnetic interference can derail your PCB’s performance. EMI management is not just a technical necessity but a hallmark of exceptional PCB design.

CUTTING COSTS, NOT CORNERS: Building Large Scale Applications With Open Source Software
Here are some strategies and best practices for leveraging open source to create enterprise-grade web and mobile applications without sacrificing quality or functionality.

"We Are One Of India's Very Few State Bodies To Manage The Entire Lifecycle Of The Electronics EcosystemFrom Approvals To Subsidies."
What is Gujarat State Electronics Mission GSEM), and how is it attracting major investments in electronics manufacturing, particularly semiconductor manufacturing, to Gujarat? To delve deeper, Electronics For You’s Nijhum Rudra spoke with Manish Gurwani, the head of GSEM. Here is what he revealed...