
YOUR TECHNIQUE FOCUSED ON ASTROCYTES. WHAT EXACTLY ARE THEY?
Yichao Yu: They're a type of glial cell [non-neuronal cells that are found in the brain and spinal cord]. They're very abundant, they outnumber neurons (nerve cells] many times over. Traditionally they're viewed as support cells, they recycle the neurotransmitters that neurons release. They do many logistical maintenance jobs in the brain. But in recent years, as we've learnt more about these cells, we've found that they have many other functions, such as regulating cognitive behaviour.
Mark Lythgoe: For the last hundred years they've been the second-class citizen in the brain in terms of cells. Neurons have taken the limelight because they're electrically active (send electrical signals) and supposedly control all our functions. But astrocytes, although not electrically active in the same way, can communicate and sense and process and control bodily functions.
About 30 years ago, they were called the genius cell. This is because when Einstein died in 1955, his brain was taken out by the pathologist Thomas Harvey and it remained hidden for nearly 30 years. Harvey then started to release a couple of the sections to Marian Diamond, an amazing neuroscientist. She found that Einstein did not have more neurons in certain areas of his brain. He actually had more glial cells, and because of that they were known as the genius cell.
WHAT ARE THE MICRO MAGNETS THAT YOU USE MADE FROM?
YY: They're very simple magnetic particles. They have a core that is made of iron oxide and a polymer shell, which enables us to attach various things to their surface. For example, we attach the antibody to the surface of these magnetic particles so that they will be targeted to astrocytes specifically.
Denne historien er fra March 2022-utgaven av BBC Science Focus.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent ? Logg på
Denne historien er fra March 2022-utgaven av BBC Science Focus.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent? Logg på

THE WORST IDEAS OF THE 21ST CENTURY
NOT ALL IDEAS CAN BE HITS. ALONGSIDE GROUND-BREAKING INNOVATIONS, 21ST-CENTURY SCIENTISTS HAVE HELMED THEIR SHARE OF WILD TECH FLOPS, DUBIOUS THEORIES AND OVERHYPED BREAKTHROUGHS. HERE ARE THE BIGGEST TO FORGET

10 IDEAS THAT WILL SHAPE YOUR NEXT 25 YEARS
Predicting the future is considered a fool's game. But it's one many of us like to play.

THE BIGGEST BREAKTHROUGHS OF THE CENTURY
We're a quarter of the way into the new century. To mark this milestone, we asked the UK's top minds to highlight some of the game-changing scientific breakthroughs shaping our world since the year 2000

DO THE SCIENCE COGNITIVE SHUFFLE
Trouble sleeping? A lot on your mind? Use this trick and sedate your synapses
WHAT DETERMINES HOW MANY ABS I CAN GET?
Assuming you're a human being, you have exactly the same number of abs as everybody else: two.

HOW CAN I IDENTIFY MY PSYCHOLOGICAL BLIND SPOT?
In the 1950s two American psychologists, Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham, proposed a way of thinking about psychological blind spots - things you don't know about yourself - that they called the 'Johari Window' (the term is a combination of their first names).

How can I change my personality?
Want to become more confident, extroverted or assertive? Science shows that with a few simple changes, you can unlock your best self

Could your cosmetics be harming your health?
Cosmetic companies are phasing out microplastics and so-called 'forever chemicals' to help protect consumers.

extraterrestrial US Congress is talking about activity again. Is the truth really out there?
Despite several testimonies, the question remains frustratingly unanswered
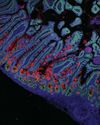
Map of 100 million human body cells revealed
Over three dozen new studies mark significant milestone towards complete Human Cell Atlas