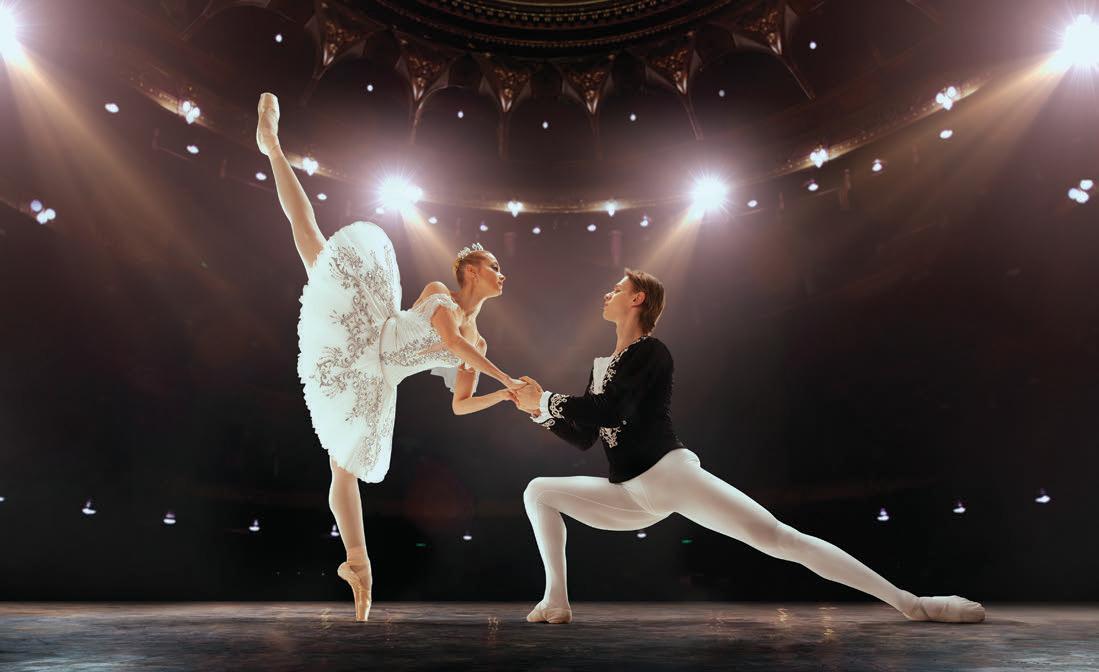

In the ballet The Nutcracker, the magician Drosselmeyer draws Clara into a magical adventure. She breaks the spell that turned Hans-Peter into the Nutcracker Doll. As Clara and a liberated Hans-Peter enter the magical "Land of Snow," snow falls in an enchanted forest in celebration of the boy's return.
As 16 dancers dressed as Snowflakes create the twirling illusion of snow onstage, Clara and Hans-Peter engage in a pas-de-deux, or dance for two. They make seemingly weightless leaps into the air. The seven-minute "snow scene" leaves the audience dazzled as the curtain falls to close Act I. Some are blissfully unaware of the mental and physical prowess such rigorous ballet dancing requires.
Behind the scenes, these ballet dancers have turned to sports science to help them achieve their peak performances and protect themselves from injury. A growing number of elite ballet dancers now see themselves as not just performing artists but also dancing athletes.
A Centuries-Old Tradition
Part of the magical beauty of classical ballet is that it looks effortless. But nothing could be further from the truth. Building on a centuries-old tradition, dancers typically spend much of their childhood in intense ballet training to develop slender muscular bodies and maximize their coordination and flexibility. They learn to balance on their toes, defy gravity as they jump, and make endless pirouettes-spinning on one foot. Then, as professionals, ballet dancers spend all day long in classes and rehearsals. They practice multiple roles and choreographed dance routines, until everything looks perfect for the evening performance.
This story is from the May/June 2023 edition of Muse Science Magazine for Kids.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the May/June 2023 edition of Muse Science Magazine for Kids.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

A 12-Year-Old Girl's Election Sticker Is a Winner
VOTING IS A FUNDAMENTAL FREEDOM FOR AMERICANS, A MEANS OF DOING ONE'S CIVIC DUTY AND A WAY AN INDIVIDUAL CAN EXPRESS THEIR VOICE. In 1971, the United States lowered its voting age to 18. But that doesn't mean kids and teens under 18 can't participate in elections in various ways.
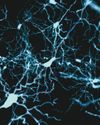
If everything the human brain does is basically sets of electrical impulses, how exactly does that translate into a state of mind?
You're not the only one asking this question. Every neuroscientist in the world is wondering the exact same thing, says Zach Mainen

EARTH'S TINIEST BUILDERS
THE HIDDEN WORLD OF MICROBES IN THE EARTH'S CRUST

MUMMIES SPEAK
ABOUT MICROBES, MIGRATION, AND MORE

GOING WITH YOUR GUT
HOW DO MICROBES AFFECT OUR HEALTH? LET'S COUNT THE WAYS...

BUG Detective
A burglar sneaks into a house on a quiet street in New York City. He walks through the house, touching countertops and door handles. Finally, he steals a single card from a full deck. Then he leaves.

Little Creatures Among Us THE MANY MICROBES IN OUR DAILY LIVES
When you think you're alone, you're actually not. In the ground, the air, your room, and even your body are Strillions and trillions of creatures so tiny you can't see them.

A Mars Rock Found With Leopard Spots Could Be a Sign of Ancient Life
IN JULY, NASA'S PERSEVERANCE ROVER CAME ACROSS A SPOTTED ROCK IN WHAT WAS ONCE A RIVERBED IN THE JEZERO CRATER ON MARS.

Para Athlete Uses Exoskeleton Suit to Carry the Olympic Torch
In July, a 36-year-old French tennis para athlete, Kevin Piette, got a chance to participate in this summer’s Olympic torch relay without using a wheelchair.

Ancient Egyptians May Have Used a Water System to Lift Stones to Build Pyramid
HOW ANCIENT EGYPTIANS BUILT THE MASSIVE PYRAMIDS IN EGYPT MORE THAN 4,000 YEARS AGO HAS LONG BEEN A TOPIC OF WONDER AND DEBATE.