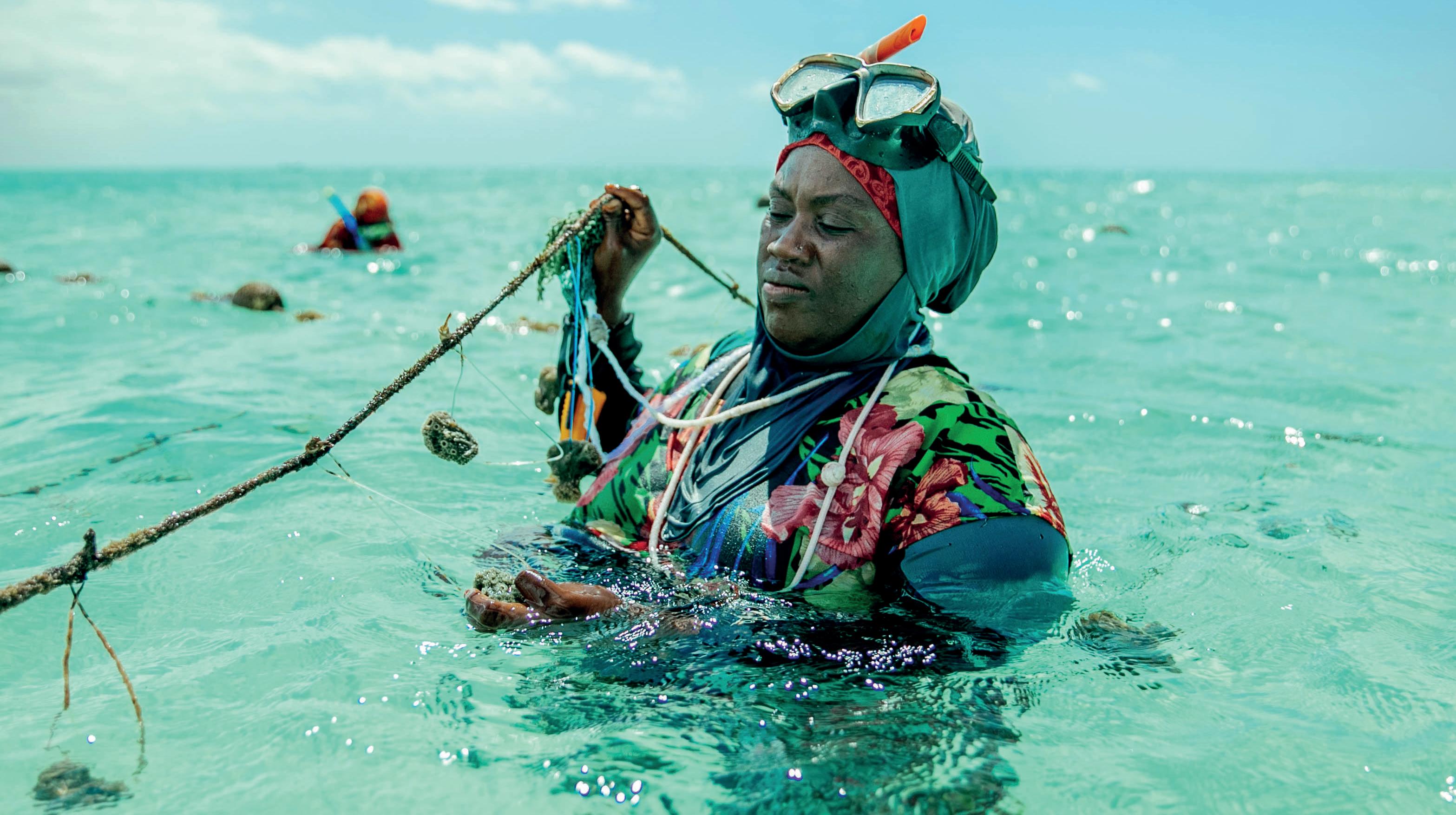

AMID THE refreshing breeze caressing Zanzibar's Jambiani coast, Hindu Rajabu wades through knee-deep water to a lagoon. Wearing swimming goggles and a snorkel perched on her headscarf, the 31-year-old mother of two cautiously navigates the Indian Ocean to locate her floating sponge farm.
Rajabu is among a handful of women in Jambiani village who in 2020 started to cultivate natural sponges. These fascinating animals are made of loosely arranged cells that surround a skeleton of fibres. The specialised cells, nestled within thousands of tiny chambers, act as microscopic pumps, tirelessly drawing water into the sponge's body with their whip-like tails. This unique pumping mechanism, which helps sponges extract nutrition and oxygen, also purifies the ocean water by removing impurities, including sewage. These sponges are also used for bathing and general hygiene because they are naturally antibacterial and antifungal and can resist odours.
With the tide gently rising, Rajabu submerges herself to reach the buoys cradling the sponge farm. Carefully, she inspects the sponges, suspended from thick polyethylene ropes. Using a knife, she removes any fouling organisms, such as bacteria and fish, which have attached themselves to the ropes. This periodic cleaning is essential to prevent the sponges from being overwhelmed by these unwanted inhabitants. The sponge farms are made of multiple ropes that run parallel to each other. They have sponges at different development stages. "We usually harvest them once a week when we collect the sponges that are big enough to be sold in the market," says Rajabu. Women typically dive deep into the ocean to collect healthy wild sponges, which serve as the foundation for their farms that are set up close to the seashore where water is up to two metres deep. These sponge colonies are then carefully cultivated and fragmented to promote new growth.
This story is from the December 16, 2023 edition of Down To Earth.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the December 16, 2023 edition of Down To Earth.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

Lifting a curse
How Gangabai Rajput helped her water-scarce village in Madhya Pradesh let go of superstition and revive an ancient waterbody

CLIMATE SHAPES SPECIES
Gradual changes in a population that lives in a region with environmental shifts give rise to new species

LEAFY GOODNESS
Leaves of the bottle gourd can be a healthy green addition to the plate

'Story of human origin is still not figured out or over'
Fifty years ago, the discovery of a partial skeleton amid the barren desert landscape of northern Ethiopia transformed our understanding of where humans came from, and how we developed into Homo sapiens. \"Lucy\" was first spotted on November 24, 1974, by the American paleoanthropologist Donald Johanson and his student assistant Tom Gray. Named after the Beatles' Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds, a popular song in the their team's camp at the time, it was immediately clear she was a female, because of her small adult size, and that she had walked upright, unlike chimpanzees. Lucy was also very old-at almost 3.2 million years, she was anointed as the then-earliest known (distant) ancestor of modern humans. Over the following decades, rather fittingly given her name, she became a \"paleo-rock star\", going on a US tour from 2006 following a deal with the Ethiopian authorities.

Deadly discharge
Residents of an industrial cluster blame effluent and sewage treatment plants for discharging poorly treated water that contaminates the area, causes skin diseases

US drug regulator faces Trump heat
FAILED REPUBLICAN presidential candidate Vivek Ramaswamy is making more news now than during his doomed attempt to get the party nomination for president. Ramaswamy's decision to throw in the towel and back Donald Trump after his campaign went nowhere showed acumen, the kind he is famous for in the investment world.

Distorted picture
India's groundwater recovery may be misleading, as new assessment methods inflate annual recharge figures and discontinue on-ground verification
A MAKE OR BREAK YEAR
Expect some stiff targets, radical policy measures and rapid innovations as polycrisis reaches a crescendo this year

Commons in crisis
A landmark 2011 Supreme Court ruling to protect shared resources deepens struggles for India's marginalised communities

Europe faces Russian natural gas supply cuts
UKRAINE'S PRIME Minister Denys Shmyhal said on December 16, 2024, that its gas transit agreement with Russia will expire on January 1, 2025, and will not be renewed. The agreement was to allow transit of natural gas to Europe amid the RussiaUkraine conflict.