
These contaminants often originating from industrial processes, mining activities and agricultural runoff pose significant risks to both ecosystems and human health. Conventional methods for removing heavy metals from wastewater can be costly and sometimes ineffective. In recent years there has been growing interest in the use of algae as a sustainable and efficient solution for wastewater treatment. This article explores the potential of algae in treating wastewater containing heavy metals examining their mechanisms benefits and challenges.
Mechanisms of Algal Treatment
Algae primarily microalgae and macroalgae have shown great potential in absorbing and accumulating heavy metals from wastewater. The mechanisms by which algae achieve this can be broadly categorized into biosorption and bioaccumulation.
Biosorption: Biosorption involves the passive binding of heavy metals to the surface of algal cells. This process is largely driven by the cell wall components such as polysaccharides, proteins and lipids which contain functional groups capable of binding metal ions. The efficiency of biosorption depends on various factors including the type of algae the nature of the heavy metals, pH, temperature and contact time. Algae such as Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis have demonstrated high biosorption capacities for metals like cadmium, lead and chromium.
Bioaccumulation: Bioaccumulation refers to the active absorption and internalization of toxic substances by algae cells. This process involves the transport of metal ions across the cell membrane and their subsequent sequestration in intracellular compartments.
This story is from the September - October 2024 edition of Scientific India.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the September - October 2024 edition of Scientific India.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

Building world's 1st pyramid
In a preprint study published this summer, researchers proposed that ancient Egyptians built the world's first pyramid the 4,700-year-old Step Pyramid of Djoser, which sits on Egypt's Saqqara plateau using a \"modern hydraulic system\" powered by a long-gone branch of the Nile River.
Climate change arms the world, ovarian cancer pulls the trigger.It's time we disarm them both
Climate change, driven by human activities, leads to environmental changes such as rising temperatures, altered weather patterns, and increased pollution.

Climate Change Added 18 mph to Hurricane Wind Speeds over Past 5 Years
High ocean temperatures caused by global warming boosted maximum intensities for most storms between 2019 and 2023, as well as for every 2024 hurricane.

How Indian Vulture Decline Led to 500,000 Deaths in 5 Years
Once a common sight across India, vultures were abundant scavengers, often seen circling landfills in search of carcasses.
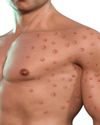
Understanding Monkeypox: Insights and Implications
Monkeypox, a viral zoonotic disease, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its re-emergence and sporadic outbreaks globally.

AI predicts that most of the world will see temperatures rise to 3°C much faster than previously expected
Three leading climate scientists have combined insights from 10 global climate models and, with the help of artificial intelligence (AI), conclude that regional warming thresholds are likely to be reached faster than previously estimated.

Infrared Radiation: A New Player In Mosquito Host-Seeking
The sound of mosquitoes is all around us when the sun sets and the air gets warm and sweltering.

Fish Oil May Benefit to Cure Alzheimer's, disorder: new findings
The benefits of fish and fish oil consumption are well-known in medical science as fish is considered a precious food resource that provides sufficient nutrition to humans.

A new class of antivirals could help prevent future pandemics
The arrival of Paxlovid in December 2021 marked another turning point in the COVID-19 pandemic an effective antiviral that has since successfully treated millions.

Turning carbon emissions into methane fuel
Chemists have developed a novel way to capture and convert carbon dioxide into methane, suggesting that future gas emissions could be converted into an alternative fuel using electricity from renewable sources. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a greenhouse gas that accounts for a large part of Earth's warming climate, and is produced by power plants, factories and various forms of transportation.