HOW TO OPERATE ON THE BRAIN
Issue 192
|How It Works UK
The procedures and surgical techniques that tackle problems inside your skull
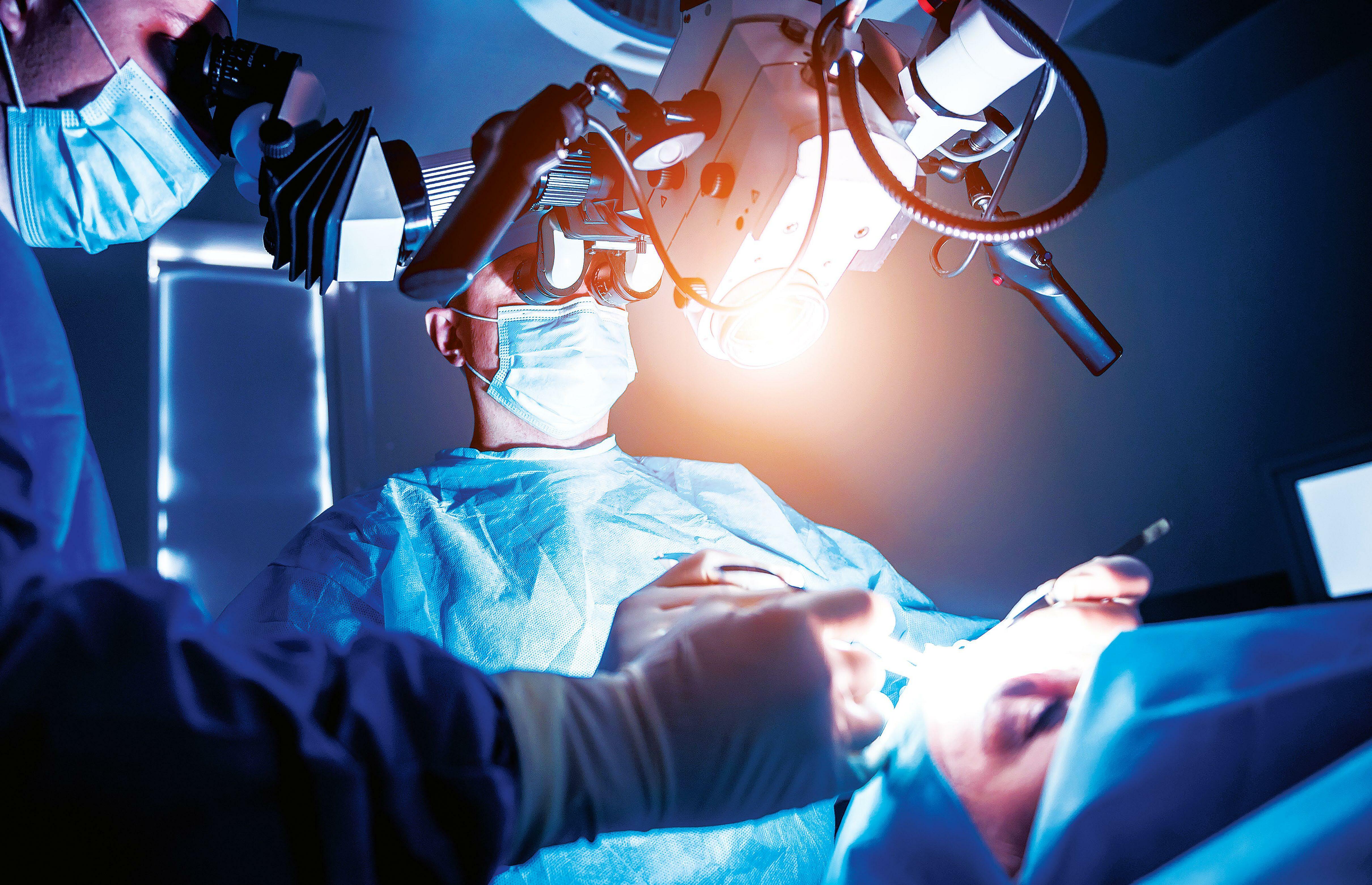
Brain surgery encompasses a myriad of procedures designed to treat an equally diverse set of conditions and associated symptoms, including tumours, blood clots, epilepsy and aneurysms. Neurosurgeries can range from minimally invasive procedures such as a biopsy, whereby a needle is inserted into the brain to collect cells for analysis, to extensive operations that expose the brain to treat blood clots and for tumour removal.
Like any other tumour, a brain tumour is an abnormal mass of cells and tissue that wedges itself somewhere in the brain. There are two categories of tumour: benign and malignant. While benign tumours can grow large, albeit slowly, they don't typically invade surrounding tissue or spread around the body. A malignant tumour, on the other hand, grows much faster, invades other tissue and can spread around the body. All in all, 120 different types of tumour can form in the brain alone.
For both benign and malignant brain tumours, a common course of intervention is a craniotomy and resection, whereby a surgeon removes a portion of the skull to expose the brain and hopefully cut away the tumour. To help guide them through the brain and keep tabs on where surgical instruments are during operations, surgeons use neuronavigation systems that are connected to their equipment.
"One of the biggest challenges is distinguishing between normal brain tissue and tumour tissue, which requires extensive training and experience," says Pietro D'Urso, a consultant neurosurgeon at Salford Royal Hospital in Manchester. "The location of the tumour is another big challenge, particularly if a tumour is in very important parts of the brain, called 'eloquent areas', that control speech and motor functions."
هذه القصة من طبعة Issue 192 من How It Works UK.
اشترك في Magzter GOLD للوصول إلى آلاف القصص المتميزة المنسقة، وأكثر من 9000 مجلة وصحيفة.
هل أنت مشترك بالفعل؟ تسجيل الدخول
المزيد من القصص من How It Works UK
How It Works UK
20 WEARABLE HEALTH TRACKERS
Whether you strap a wellness coach to your wrist or weave subtle sensors into your clothes, these devices are revolutionising how we track our health
9 mins
Issue 210
How It Works UK
SUPERPOWERED PLANTS
The world of plants is vibrant and diverse, just like this book.
1 min
Issue 210
How It Works UK
SECRET STORIES OF LOST BEASTS
We're all aware of the mighty dinosaurs that once roamed Earth, but there are so many weird and wonderful species that have been lost to time.
1 min
Issue 210

How It Works UK
ALL ABOUT BLIMPS
Is it a bird? Is it a spaceship? No... it's a non-rigid airship
2 mins
Issue 210
How It Works UK
SUPER QUESTERS MISSION: RAINFOREST MAGIC
Join adventurers Leo, Lilli and Bea as they transform into superheroes and journey to the rainforest in the pursuit of knowledge.
1 min
Issue 210

How It Works UK
HOW THE MIGHTY MAMMOTH RULED THE ICE AGE
Meet the prehistoric giants that roamed the Arctic Circle thousands of years ago
4 mins
Issue 210
How It Works UK
Have they found LIFE ON MARS?
Although it's by no means certain, scientists are slowly accumulating evidence that life once existed on the Red Planet
2 mins
Issue 210

How It Works UK
HOW FAST DO GLACIERS MOVE?
The speed at which a glacier flows depends on its mass, the depth and slope of the underlying rock bed and friction.
1 min
Issue 210

How It Works UK
HOW IN-FLIGHT WI-FI WORKS
This technology allows you to scroll to your heart's content while killing time at cruise altitude
3 mins
Issue 210

How It Works UK
HOW WIGWAMS WERE BUILT
Discover the construction and living conditions inside these traditional domed dwellings
1 mins
Issue 210
Listen
Translate
Change font size

