Science’s global revolution
BBC History UK
|October 2022
James Poskett introduces some brilliant thinkers who shatter the theory that, when it came to the scientific revolution of the 16th to 18th centuries, Europe was at the centre of the universe
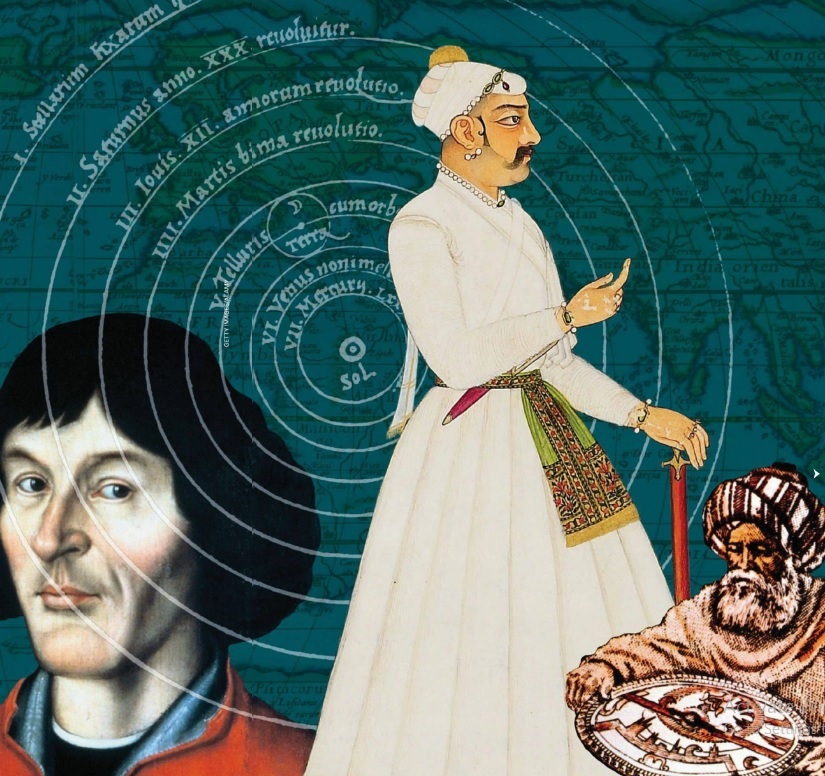
When we think of a lone scientific genius, we usually think of someone like the Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus. Working away in isolation amid the grandeur of Frombork Cathedral, Copernicus developed a radical new scientific theory.
In On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres, published in 1543, Copernicus challenged ancient tradition by putting the Sun, rather than the Earth, at the centre of the universe. This marked the beginning of what is often called the “scientific revolution”, the period between around 1500 and 1700 when European thinkers made incredible progress. This was the age of the Italian mathematician Galileo Galilei, who first observed the moons of Jupiter, and the English mathematician Isaac Newton, who first set out the laws of motion. Copernicus, like Galileo and Newton, forged ahead with a bold new scientific theory.
There is, however, a big problem with this account of the origins of modern science. By focusing on a few European geniuses, we miss a much more diverse and global story. We also give the impression that science is separate from history, that it develops independently of wider world events. In fact, science is just as much a part of world history as art, religion, culture, and politics.
Copernicus may have been a genius, but he was far from isolated. He wrote at a time when Europe was forging new connections with Asia, with caravans travelling along the Silk Road and galleons crossing the Indian Ocean.
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der October 2022-Ausgabe von BBC History UK.
Abonnieren Sie Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierter Premium-Geschichten und über 9.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Sie sind bereits Abonnent? Anmelden
WEITERE GESCHICHTEN VON BBC History UK

BBC History UK
On the skids
Richard Rodgers and Oscar Hammerstein II's smash musical Oklahoma! opened on Broadway on 31 March 1943.
1 min
Christmas 2025

BBC History UK
Small pleasures
Memory is imperfect, but what if you could get a professional model maker to recreate a moment from the past?
1 min
Christmas 2025

BBC History UK
Bath in five places
In the Georgian era, Bath became arguably Britain's most fashionable destination. KIRSTEN ELLIOTT promenades five historic highlights
3 mins
Christmas 2025

BBC History UK
End times
Why do civilisations that dominated their epoch fail? In an era of autocracy, climate change, the rise of Al and a first-hand understanding of how deadly pandemics can be, it's a question that seems pertinent.
1 min
Christmas 2025

BBC History UK
What are the origins of the Yule Lads?
To learn about the Jólasveinar (Yule Lads), we must start with their mother, the terrifying ogress Grýla. Her name appeared in Icelandic texts as early as the 13th century, although it wasn’t until later that those 13 mischievous lads became associated with her. Folk tales and poems tell how she descends from the mountains with an empty sack to stuff full of children. Grýla owns the monstrous Jólaköttur (Yule Cat), which roams the countryside on Christmas Eve, searching for children to gobble up if they're not wearing new clothes.
1 mins
Christmas 2025

BBC History UK
Santa Claus v Father Christmas
The true identity of the white-bearded, red-robed figure who fills children's stockings at Christmas has long been debated. Thomas Ruys Smith sizes up the merry contenders
8 mins
Christmas 2025

BBC History UK
Frontier friction
Set in Washington Territory in 1854, The Abandons is a Western that's unusual for having two matriarchs, women whose lives become entangled, at its centre.
1 min
Christmas 2025

BBC History UK
The Last Days of Pompeii: The Immersive Experience
Delve into the culture of daily Roman life, witness the momentous eruption of Mount Vesuvius, and follow its fallout in Immerse LDN's new exhibition. In a blend of cutting-edge technology and vivid storytelling, this exhibition launches visitors into Pompeii's rich history with recreations of the ancient city's beautiful pre-eruption landscape, a 360-degree virtual reality Roman amphitheatre experience, and a digital metaverse recreating Pompeii's 'Villa of Mysteries'.
1 min
Christmas 2025

BBC History UK
Elizabeth Marsh The corsair's captive
Taken hostage by a Barbary ship's captain in the 18th century, a young Englishwoman found herself fighting for her freedom in Marrakech. ADAM NICHOLS introduces a brave captive who later wrote a book about her dramatic experiences
6 mins
Christmas 2025

BBC History UK
29 DECEMBER 1170: Thomas Becket is murdered in Canterbury
Knights loyal to Henry II rid him of the “low-born cleric”
2 mins
Christmas 2025
Translate
Change font size

