Versuchen GOLD - Frei
PRIME TRIGGER
Down To Earth
|April 16, 2024
Heat stress dominates debate on the causes of a mysterious chronic kidney disease that continues to baffle health experts and is on the rise globally
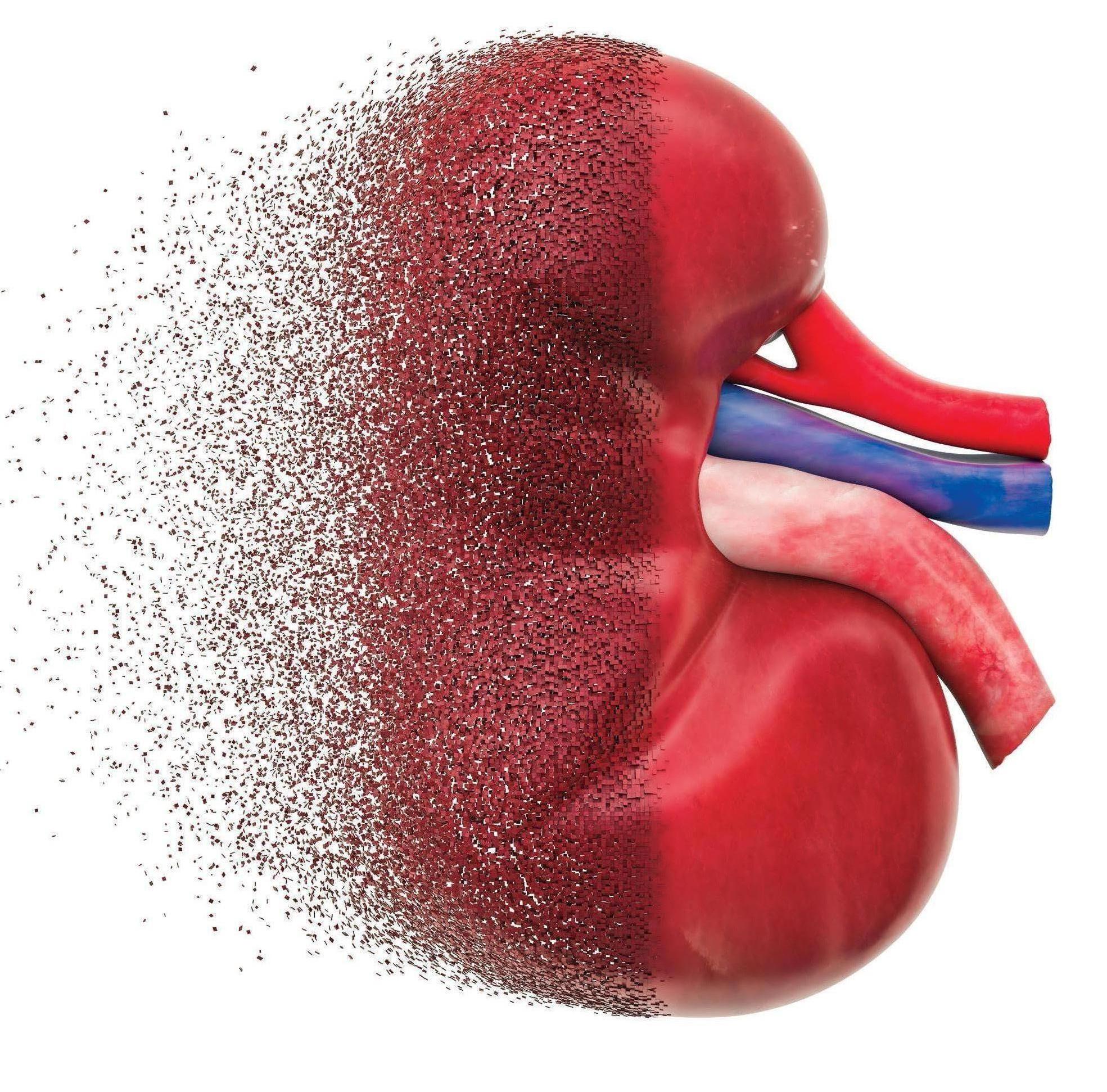
MORE THAN 30 years and 35 countries. These are the only definitive data available about the chronic kidney disease of unknown origin or CKDU-a condition whose mysterious nature is evident from its name.
Chronic kidney disease, which is characterised by progressive loss of kidney function, is usually reported among those suffering from diabetes, hypertension and glomerulonephritis (a type of kidney inflammation), or those who have inherited genetic diseases that damage this key filter system of the body. But scientists have so far not been able to pinpoint what causes CKDU. This knowledge gap hampers efforts to prevent new cases and slow progression of the disease, which can be fatal. Doctors say the condition usually remains undiagnosed until kidney failure.. What's alarming is that the prevalence of CKDU is on the rise globally.
CKDU was first identified in Sri Lanka and India in the 1990s. Soon, the disease was also reported from Central American countries. According to a review paper published in Environmental Geochemistry and Health on September 12, 2022, CKDU was initially limited to tropical countries. But in the last three decades, it has been reported from 35 countries, including the US and UK. Though no data is available on the global burden of CKDU, the paper estimates that the disease could be responsible for over 30,000 deaths a year and that Sri Lanka and India have the highest number of people affected by CKDU.
According to the Indian Chronic Kidney Disease Burden 2022, published in Clinical Kidney Journal, 19.5 per cent of all chronic kidney disease patients in the country are classified as CKDU. The rate is on par with chronic kidney disease triggered by diabetes (24.9 per cent) and by cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (23.2 per cent), characterised by abnormal growth of cells on cervix.
Diese Geschichte stammt aus der April 16, 2024-Ausgabe von Down To Earth.
Abonnieren Sie Magzter GOLD, um auf Tausende kuratierter Premium-Geschichten und über 9.000 Zeitschriften und Zeitungen zuzugreifen.
Sie sind bereits Abonnent? Anmelden
WEITERE GESCHICHTEN VON Down To Earth
Down To Earth
China backs open-source AI to circumvent US checks
CHINA IS challenging global artificial intelligence (AI) dynamics by releasing powerful, open-source models developed by its tech giants, including Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent and the startup DeepSeek. This strategic move aims to circumvent US export restrictions on advanced chips and to foster rapid innovation within its AI sector.
1 min
July 01, 2025

Down To Earth
Yet another washout
UN Ocean Conference sees limited progress, as SDG 14 remains the least funded global goal despite pledges and finance talks
6 mins
July 01, 2025
Down To Earth
WHAT IS THE DEBT AND CLIMATE LINK?
Over half of the low- and middle-income nations with high climate vulnerability are either already in debt distress or at high risk of it
5 mins
July 01, 2025
Down To Earth
India rolls out guidelines for expired medicine
ON MAY 26, India's Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation issued guidelines for the safe disposal of expired and unused medicines to drug controllers in all states and Union Territories.
1 min
July 01, 2025
Down To Earth
TAME THE TRADE
Strengthen wildlife protection laws to combat illegal hunting and trade of exotic and threatened species in India
4 mins
July 01, 2025
Down To Earth
13 nations battle hunger emergencies
THE WORLD stands on the brink of yet another humanitarian disaster with at least 13 countries facing escalating hunger emergencies-five of which are on the verge of famine.
1 min
July 01, 2025

Down To Earth
HOW LARGE IS SOVEREIGN DEBT?
Its burden on developing countries is growing twice as fast as on developed countries
4 mins
July 01, 2025

Down To Earth
A grove revived
It took 15 years for residents of Rajasthan's Sirawas village to bring to life a severely degraded sacred grove, an initiative that has triggered replicative efforts across the region
4 mins
July 01, 2025
Down To Earth
WHY SOVEREIGN DEBT RISING IN DEVELOPING WORLD?
Biased sovereign credit ratings and steep interest rates are at work
4 mins
July 01, 2025
Down To Earth
WHAT ARE THE SPILLOVER IMPACTS OF EXTERNAL DEBT?
Development priorities put on back burner
2 mins
July 01, 2025
