
INDIA STANDS AT the threshold of significant economic growth. By 2047, the country aims to transform into a $30 trillion economy, achieving the status of a developed nation and attaining energy independence. The nation’s GDP is projected to double from the current $3.6 trillion by 2030, and another 200 million people are expected to be added to the current 1.4 billion in the next three decades.
To support this growth and enhance the standard of living for its citizens, India is making substantial investments in energy, transportation and urban infrastructure. However, this transformation is unfolding against the backdrop of global climate change, necessitating sustainable, resilient and inclusive development strategies.
In 2021, India ranked as the 7th most vulnerable country to climate change and, in the same year, suffered losses of $159 billion due to extreme heat. As many as 17 of 20 Indians are vulnerable to extreme hydro-meteorological disasters. A disproportionate amount of this burden is borne by vulnerable communities—49 per cent of urban Indians live in informal settlements, with unequal access to basic services, decent work and safe, healthy environments. The annual monsoons, on which the country’s agrarian economy is largely dependent, have become unpredictable, impacting food production and nutritional security, especially of small and marginal land holders.
TRANSITIONING TOWARDS CLEAN ENERGY
More than 745 million people globally still lack access to electricity. At the same time, energy is responsible for 73 per cent of global greenhouse gas emissions.
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

Constipation Can Put Your Heart At Risk
PEOPLE WITH CONSTIPATION have an increased risk of major cardiac events, including heart attack, stroke and heart failure, especially if they also have high blood pressure, finds an international study published in the American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology.

Too Much Sitting Can Accelerate Ageing
SITTING FOR EXTENDED PERIODS can harm the heart and accelerate ageing, even if you are young and get the minimum recommended amount of daily exercise, according to a US study published in the journal PLOS One.
Efficiency and innovation
As health care evolves, professionals must employ innovative methods to refine their skills
Level up
Only 30 per cent of needy patients are able to undergo transplant in India; we need more dedicated transplant centres

HOPE STEMS FROM A CELL
While stem cell therapies have shown success in treating blood disorders, orthopaedic ailments, autoimmune diseases and eye issues, there is hope that they can one day treat patients with heart disease, blindness, Parkinson's, HIV, diabetes and spinal cord injuries

Mind matters
Your mindset can limit or expand your physical ability

Cutting edge
Would you go under the knife if a robot was the one holding it? Or would you say, \"No way, I need a human touch\"? You might have to decide soon because a robot that can imitate skilled human surgeons is already here.
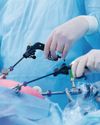
The smallest cut
Minimally invasive surgeries have a bright future, with virtual reality and 3D procedures offering greater precision and AI on the horizon

Signalling a revolution
Canadian scientist and entrepreneur Sachdev Sidhu is focused on bringing cutting-edge antibody engineering to his country of origin

Wellness on demand
Starting as a doctor-patient chat platform, Medibuddy has evolved to be India's largest on-demand, full-stack digital health care platform