
It had been 48 hours since we began looking for the elusive trapdoor spider. Four of us, including scientist Akshay Khandekar, were crouched on the ground littered with dry leaves, staring at a mound of soil under a tree. Silence was key. We were in Amboli forest, a protected reserve in Maharashtra’s Sindhudurg district, some 700m above sea level. This area falls under the jurisdiction of the Sawantwadi Forest Department. Mercury was at 34 degrees Celsius. Sticky heat.
As we closed in on 20 minutes on our haunches, Khandekar inspected the soil under the bark of a tree with his little finger, very lightly, as if caressing a newborn. Nothing happened. We moved on.
In 2020, this was the very spot where Khandekar, 31, discovered the first trapdoor spider species from the Western Ghats. That moment was historic and rewarding, but the search had been frustrating and time-consuming, as it was now. Then, it had taken him three months to find one specimen of the spider—he named it Conothele Ogalei, after his friend and fellow researcher Hemant Ogale.
Khandekar, a field biologist and taxonomist, had read that there are about 35 species of the trapdoor spider spread across south, central and northeast India, but the genus Conothele had never been found in the Western Ghats. He decided he was the man for the job.
But that is the problem with trapdoors; they are not meant to be found. These elusive creatures dig into the ground and, at the entrance of the burrow, build silken-hinged trapdoors. They feed by quickly opening the door and grabbing insects passing by.
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

Too Much Sitting Can Accelerate Ageing
SITTING FOR EXTENDED PERIODS can harm the heart and accelerate ageing, even if you are young and get the minimum recommended amount of daily exercise, according to a US study published in the journal PLOS One.
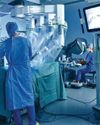
Efficiency and innovation
As health care evolves, professionals must employ innovative methods to refine their skills
Level up
Only 30 per cent of needy patients are able to undergo transplant in India; we need more dedicated transplant centres

HOPE STEMS FROM A CELL
While stem cell therapies have shown success in treating blood disorders, orthopaedic ailments, autoimmune diseases and eye issues, there is hope that they can one day treat patients with heart disease, blindness, Parkinson's, HIV, diabetes and spinal cord injuries

Mind matters
Your mindset can limit or expand your physical ability

Cutting edge
Would you go under the knife if a robot was the one holding it? Or would you say, \"No way, I need a human touch\"? You might have to decide soon because a robot that can imitate skilled human surgeons is already here.
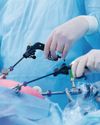
The smallest cut
Minimally invasive surgeries have a bright future, with virtual reality and 3D procedures offering greater precision and AI on the horizon

Signalling a revolution
Canadian scientist and entrepreneur Sachdev Sidhu is focused on bringing cutting-edge antibody engineering to his country of origin

Wellness on demand
Starting as a doctor-patient chat platform, Medibuddy has evolved to be India's largest on-demand, full-stack digital health care platform

HEARING AND VISION LOSS LINKED TO HEART DISEASE AND STROKE
A CHINESE STUDY PUBLISHED IN THE JOURNAL of the American Heart Association suggests that middle aged and older adults with sensory impairments, specifically hearing and vision loss, have an elevated risk of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke and heart attacks.