
IT IS A FORTUITOUS coincidence that the NITI Aayog has just released its approach paper on a “Vision for Viksit Bharat@2047”, the year marking the 100th anniversary of India’s independence. In exploring what India’s international role and status would be in that year, one may note certain key assumptions and projections contained in the paper.
The “Vision” sets the goal of our national endeavours at becoming a developed nation, for which “we need to strive to be a $30 trillion economy by 2047 with a per capita income of $18,000 ( ₹15 lakh) per annum. The GDP would have to grow nine times from today’s $3.36 trillion and the per capita income would need to rise eight times from today’s $2,392 ( ₹2 lakh) per annum.”
The paper declares: “In a Viksit Bharat, the economy will be a leading global economy, a driver of global economic growth, a magnet of global talent, trade and capital. Its cities and markets will be among the largest and top-most business and financial centres of the world.” Further, there will be “Indian-origin Global Business Champions in manufacturing, services, agriculture, R&D and innovation, technology and scale.”
These projections would make India the third largest economy in 2047 behind China and the US, but what would be the gap with these two powers? It is the relative equation which matters. The Indian economy may end up half as large as China’s, and two-thirds of the US. Projected to grow faster than both China and the US, India would have shrunk the gap with both countries and this will bestow greater agency on it in the shaping and management of the international order by mid-century.
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the {{IssueName}} edition of {{MagazineName}}.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

Hat-Trick Or Has-Beens?
India look to win their third straight Test series in Australia, but ageing superstars and recent humiliation at home have cast a shadow on their hopes

Constipation Can Put Your Heart At Risk
PEOPLE WITH CONSTIPATION have an increased risk of major cardiac events, including heart attack, stroke and heart failure, especially if they also have high blood pressure, finds an international study published in the American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology.

Too Much Sitting Can Accelerate Ageing
SITTING FOR EXTENDED PERIODS can harm the heart and accelerate ageing, even if you are young and get the minimum recommended amount of daily exercise, according to a US study published in the journal PLOS One.
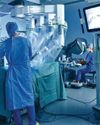
Efficiency and innovation
As health care evolves, professionals must employ innovative methods to refine their skills
Level up
Only 30 per cent of needy patients are able to undergo transplant in India; we need more dedicated transplant centres

HOPE STEMS FROM A CELL
While stem cell therapies have shown success in treating blood disorders, orthopaedic ailments, autoimmune diseases and eye issues, there is hope that they can one day treat patients with heart disease, blindness, Parkinson's, HIV, diabetes and spinal cord injuries

Mind matters
Your mindset can limit or expand your physical ability

Cutting edge
Would you go under the knife if a robot was the one holding it? Or would you say, \"No way, I need a human touch\"? You might have to decide soon because a robot that can imitate skilled human surgeons is already here.
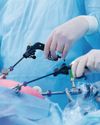
The smallest cut
Minimally invasive surgeries have a bright future, with virtual reality and 3D procedures offering greater precision and AI on the horizon

Signalling a revolution
Canadian scientist and entrepreneur Sachdev Sidhu is focused on bringing cutting-edge antibody engineering to his country of origin