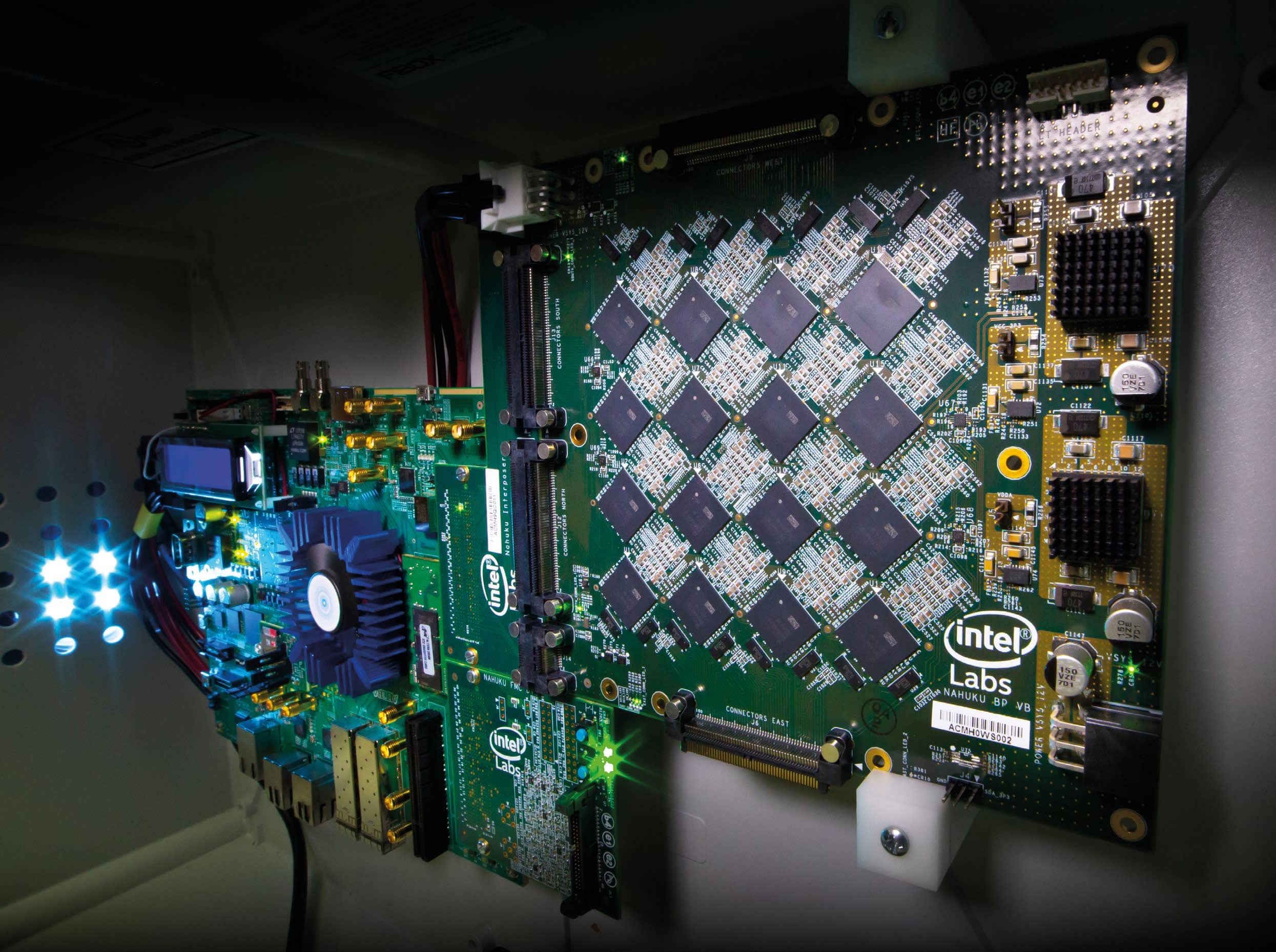
Intel loves a good codename. Who remembers Dragontail Peak? Or Lizard Head Pass? Or even 2008’s White Salmon? Great days. All of those refer to motherboards, but Pohoiki Beach is different – it’s a new way of building computers that’s based on the human brain. Neuromorphic computing – literally ‘nerve shaped’ – uses insights from neuroscience to create chip architectures.
By simulating the way human brains work in silicon, calculations can be carried out faster while using less energy. The training of neural networks can be carried out more efficiently too, with only one viewing of an object necessary for the net to recognise it forever.
Mike Davies, director of Intel’s Neuromorphic Computing Lab, sees it more clearly, “Neuromorphic computing entails nothing less than a bottom-up rethinking of computer architecture,” he says. “The goal is to create chips that function less like a classical computer and more like a human brain. Neuromorphic chips model how the brain’s neurones communicate and learn, using spikes and plastic synapses that can be modulated based on the timing of events. These chips are designed to self-organize and make decisions in response to learned patterns and associations.”
Which all sounds a bit Cyberdyne, but we’re sure this will be fine. The goal is that one-day neuromorphic chips may be able to learn as fast and efficiently as the brain, which still far outperforms today’s most powerful computers. According to Intel, neuromorphic computing could lead to advancements in robotics, smart city infrastructure, and other applications that require continuous learning and adaptation to evolving data.
この記事は PC Gamer の July 2020 版に掲載されています。
7 日間の Magzter GOLD 無料トライアルを開始して、何千もの厳選されたプレミアム ストーリー、9,000 以上の雑誌や新聞にアクセスしてください。
すでに購読者です ? サインイン
この記事は PC Gamer の July 2020 版に掲載されています。
7 日間の Magzter GOLD 無料トライアルを開始して、何千もの厳選されたプレミアム ストーリー、9,000 以上の雑誌や新聞にアクセスしてください。
すでに購読者です? サインイン

A New Dawn - The rise, fall and rise again of PC Gaming in Japan
The so-called 'Paso Kon' market (ie katakana's transliteration of 'Pasonaru Computa') in Japan was originally spearheaded in the 1980s by NEC's PC-8800 and, later, its PC-9800.

MARVEL: ULTIMATE ALLIANCE
Enter the multiverse of modness.

SLIDES RULE
Redeeming a hated puzzle mechanic with SLIDER

GODS AND MONSTERS
AGE OF MYTHOLOGY: RETOLD modernises a classic RTS with care

PHANTOM BLADE ZERO
Less Sekiro, more Wo Long: Fallen Dynasty

STARR-MAKING ROLE
Final Fantasy XVI's BEN STARR talks becoming a meme and dating summons

THIEF GOLD
Learning to forgive myself for knocking out every single guard.

HANDHELD GAMING PCs
In lieu of more powerful processors, handhelds are getting weirder

FAR FAR AWAY
STAR WARS OUTLAWS succeeds at the little things, but not much else shines

FINDING IMMORTALITY
Twenty-five years on, PLANESCAPE: TORMENT is still one of the most talked-about RPGs of all time. This is the story of how it was created as a ‘stay-busy’ project by a small team at Black Isle Studios