
I LOOK BACK with pride on the day in 1962 when I joined my first squadron at Ambala. It was a welcoming sight to see half a dozen shining Hunters neatly parked on the tarmac. Will I get a chance to fly those was the first question that came up on my mind. The Hunter-56 was one of the fastest fighter planes of that time in the IAF. My training to get operational on the aircraft went on at a slow pace and often we faced spare parts crunch. (No such difficulties exist in the IAF these days).
Post the 1962 war with China, there was a sense of fatigue all around. Yet, the attitude was positive—wondering about the next round. From then on, our military changed course steadily in the ways that they were organised, equipped, trained and fought. The 1965 war came a bit too soon—we were woefully short on military hardware and munitions. Our tactics were ancient, our aircraft lacked sensors and we had never even heard of Electronic Warfare Suit. My first air-combat was totally visual and our basic communication system gave me trouble.
In the 1970s, the government struggled to get the economy in order. The Pakistanis had the US supplied F-104 fully operational, whereas the MIG-21s of the IAF were newly inducted and their numbers were small. Our military fought gallantly in the 1971 war, defeated the Pakistanis and liberated Bangladesh.
In the mid 1990s, India changed gears on all fronts. Science and technology were given due space and importance. Yet, India remained a major importer of weapons. In the 2000s, the nation was yet to absorb the importance of self-reliance. Lack of skill combined with the urge to get government jobs made our work-force ineffective. Manufacturing sector was not given due importance. Probably it was the right time for the government to spell out its strategy of atmanirbhartha (self-reliance).
Denne historien er fra August 18, 2024-utgaven av THE WEEK India.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent ? Logg på
Denne historien er fra August 18, 2024-utgaven av THE WEEK India.
Start din 7-dagers gratis prøveperiode på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av utvalgte premiumhistorier og 9000+ magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent? Logg på
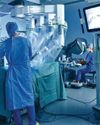
Efficiency and innovation
As health care evolves, professionals must employ innovative methods to refine their skills
Level up
Only 30 per cent of needy patients are able to undergo transplant in India; we need more dedicated transplant centres

HOPE STEMS FROM A CELL
While stem cell therapies have shown success in treating blood disorders, orthopaedic ailments, autoimmune diseases and eye issues, there is hope that they can one day treat patients with heart disease, blindness, Parkinson's, HIV, diabetes and spinal cord injuries

Mind matters
Your mindset can limit or expand your physical ability

Cutting edge
Would you go under the knife if a robot was the one holding it? Or would you say, \"No way, I need a human touch\"? You might have to decide soon because a robot that can imitate skilled human surgeons is already here.
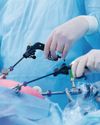
The smallest cut
Minimally invasive surgeries have a bright future, with virtual reality and 3D procedures offering greater precision and AI on the horizon

Signalling a revolution
Canadian scientist and entrepreneur Sachdev Sidhu is focused on bringing cutting-edge antibody engineering to his country of origin

Wellness on demand
Starting as a doctor-patient chat platform, Medibuddy has evolved to be India's largest on-demand, full-stack digital health care platform

HEARING AND VISION LOSS LINKED TO HEART DISEASE AND STROKE
A CHINESE STUDY PUBLISHED IN THE JOURNAL of the American Heart Association suggests that middle aged and older adults with sensory impairments, specifically hearing and vision loss, have an elevated risk of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke and heart attacks.

PETTICOAT CANCER AND THE SARI LINK
TYING YOUR UNDERSKIRT (petticoat) tightly around the waist when wearing a sari, can lead to \"petticoat cancer\" or \"sari cancer,\" as it was previously called. Tying the underskirt too tightly can cause constant cord friction that can lead to chronic inflammation, skin ulceration and, in rare cases, skin cancer.